FIGURE 2.
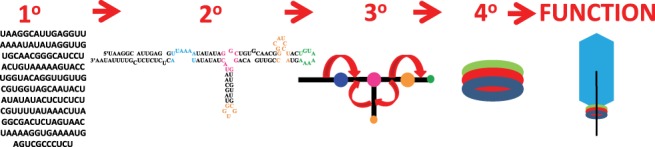
Hierarchical RNA folding. The primary structure is the sequence; in this example, the sequence of GA1 prohead RNA. The secondary structure is the pattern of Watson–Crick pairs and noncanonical motifs, such as bulge loops, multibranch loops, and hairpin loops. The primary and secondary structures for GA1 pRNA were first reported in Bailey et al. (1990). The tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of the molecule. In this ball-and-stick model of pRNA, the orientations of the helices (shown as black sticks) are flexible around the loops (shown as balls). The dynamic helical angles are represented by curly red arrows. The quaternary structure is interactions of the RNA with other RNA, protein or ligands. In the case of GA1 pRNA, the pRNA forms a ring (red circle) with a ring of ATPases (blue circle) and connector proteins (green circle). The function of GA1 pRNA is to package the bacteriophage DNA genome (black line) into a preformed capsid (blue hexagon).
