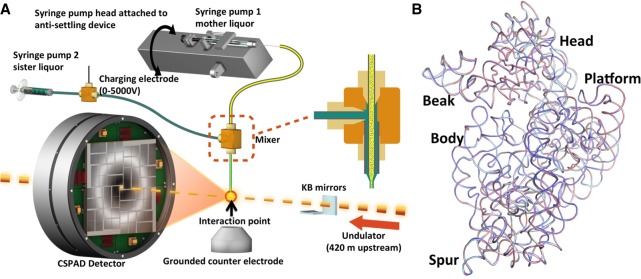
FIGURE 1.
Approach to serial femtosecond X-ray (SFX) crystallography studies of a 30S ribosomal subunit decoding complex. (A) Diagram of the concentric-flow MESH injector setup at the CXI instrument of the LCLS. The liquid jet, comprising microcrystals and their mother liquor (colored in yellow), flows in the continuous inner capillary (100 µm × 160 µm × 1.5 m; colored in gray). The sister liquor (colored in green) is charged by a high voltage power supply (0–5000 V) for electro-focusing of the liquid jet. A mixer (indicated within the dashed orange rectangle) joins the two capillaries (colored in gray) concentrically. The sample reservoir containing ribosome microcrystals is mounted on an anti-settling device, which rotates, at an angle, about the capillary axis to keep the microcrystals suspended homogenously in the slurry. The liquid jet and the LCLS pulses interact at the point indicated by the orange circle. (B) Comparison of T. thermophilus 30S-ASL-mRNA-paromomycin complex structures. Superposition of 16S rRNA backbones from cryo-cooled structures colored in cyan and slate (PDB IDs: 4DR4 and 1IBL, respectively) with the ambient-temperature structure colored in salmon. The positions of the major 30S domains are indicated. All X-ray crystal structure figures are produced with PyMOL (http://www.schrodinger.com/pymol).