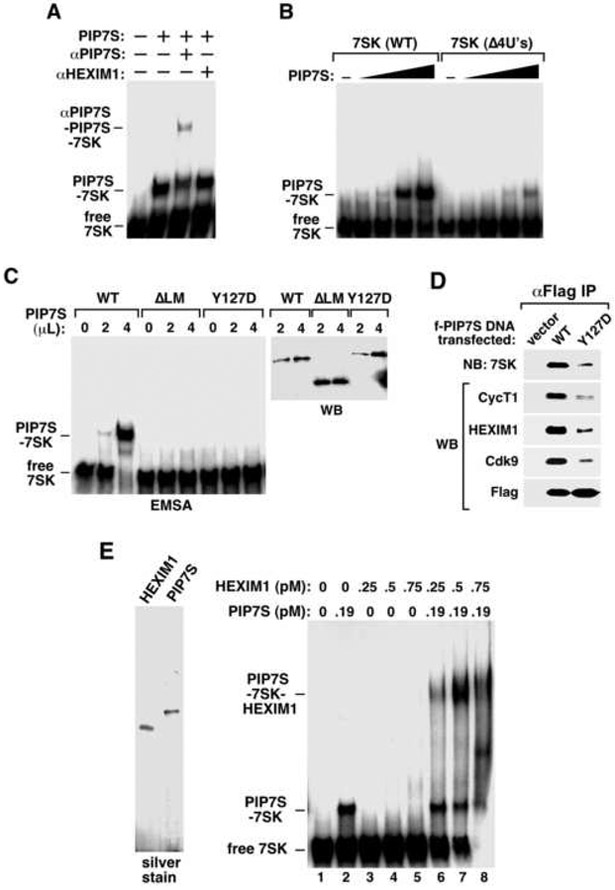
Figure 3. The 7SK-PIP7S binding requires both the poly(U) tail of 7SK and the La domain of PIP7S and recruits HEXIM1 to 7SK snRNP.
A. Affinity-purified PIP7S, anti-PIP7S (αPIP7S) and anti-HEXIM1 (aHEXIM1) antibodies were incubated as indicated with 32P-labeled 7SK and analyzed by EMSA. B. Wild-type 7SK or its mutant Δ4U’s was added to EMSA reactions containing increasing amounts of PIP7S (in 2-fold increments). C. Flag-tagged wild-type PIP7S and its mutants ΔLM and Y127D were affinity-purified, adjusted to similar concentrations by anti-Flag western blotting (right), and analyzed for their interactions with 7SK by EMSA (left). D. Flag-tagged wild-type PIP7S or Y127D was expressed in HeLa cells. Anti-Flag IP derived from NEs was analyzed by western (WB) and northern blotting (NB) as indicated. E. Left: Flag-tagged HEXIM1 and PIP7S were affinity-purified from transfected HeLa cells and examined on a silver-stained SDS-gel. Right: The two proteins were added at the indicated concentrations to EMSA reactions containing 32P-labeled 7SK.