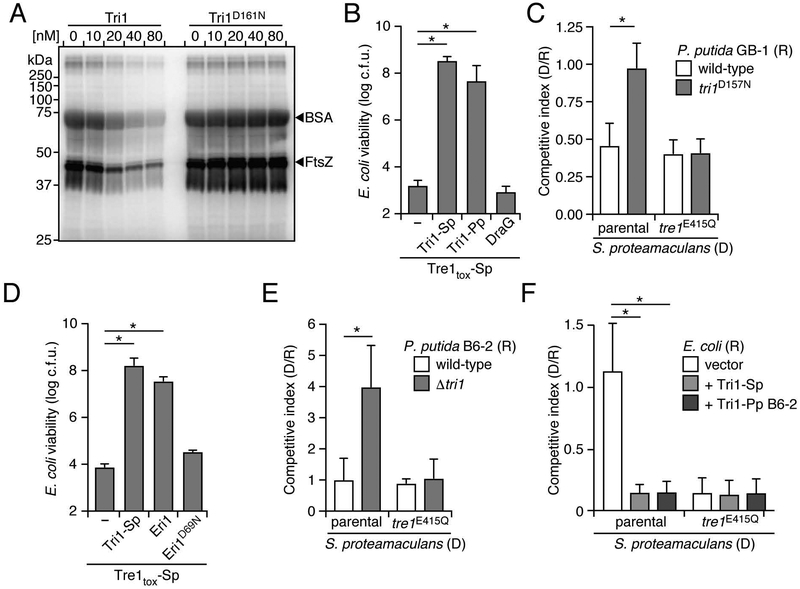
Figure 6.
ARH domain-containing immunity proteins provide protection from non-cognate ART toxins. (A) Autoradiograph of SDS-resolved products resulting from incubating a mixture of FtsZ and BSA (1:16 ratio) with Tre1tox and [adenylate-32P]-NAD+ to facilitate ADPr, followed by treatment with the indicated Tri1 proteins. (B and D) Viable E. coli recovered from populations expressing Tre1tox-Sp and the indicated ARH-domain proteins. (C) Competitiveness of the indicated donor (D) strains of S. proteamaculans toward wild-type or a tri1 mutant of P. putida GB-1, after 6 h coculture on a solid medium. (E) Competitiveness of indicated donor strains of S. proteamaculans toward the noted recipient strains of P. putida B6–2 as grown in C. (F) Competitiveness of S. proteamaculans toward E. coli heterologously expressing a vector control, Tri1 from S. proteamaculans or Tri1 from P. putida B6–2, grown as in C. Data in B-F represent means ± SD. Asterisks in B-F indicate statistically significant differences between the indicated mean values (p<0.05, n = 3). See also Figure S4.