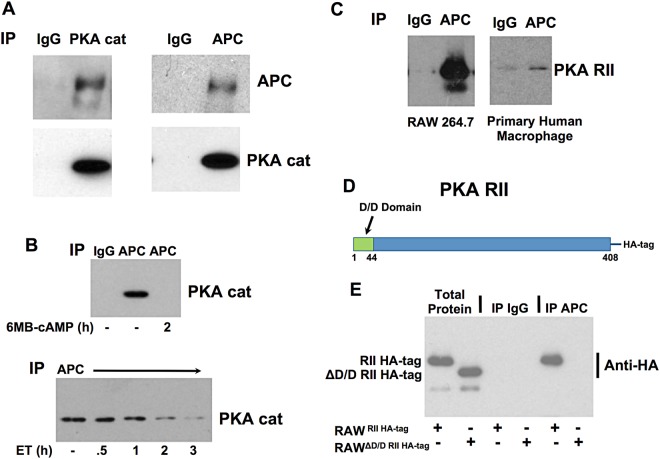
Figure 8.
APC binds PKA and responses to cAMP. Panel (A) APC binds PKA cat in RAW 264.7 cells. Immunoprecipitations were executed with control rabbit IgG, rabbit IgG against APC, or rabbit IgG against PKA cat α. The subsequent immunoblots were probed with antibodies against APC or PKA cat α. Panel (B) Elevated cAMP in macrophages leads to the release of PKA cat α from APC. Immunoprecipitations were performed using protein extracts taken from RAW 264.7 cells exposed 1 mM 6-MB-cAMP or 10 nM ET. Immunoprecipitations were carried out with control rabbit IgG or rabbit IgG against APC. The immunoblots were probed with antibodies recognizing PKA cat α. Panel (C) APC binds PKA RII in RAW 264.7 cells and human monocytes. Immunoprecipitations were performed using protein extracts from RAW 264.7 cells or primary human macrophages using control IgG or IgG against APC, and immunoblots were probed with antibodies recognizing PKA RII. Panel (D) Domain layout of PKA RII highlighting the docking and dimerization (D/D) domain that is deleted from PKA RII. Panel (E) RAW 264.7 cells were transduced with a replication incompetent retrovirus containing RII HA-tagged or ΔD/D RII HA-tagged. Immunoprecipitations were then performed with control rabbit IgG or rabbit IgG against APC. The immunoblots were probed with antibodies recognizing the HA-tag.