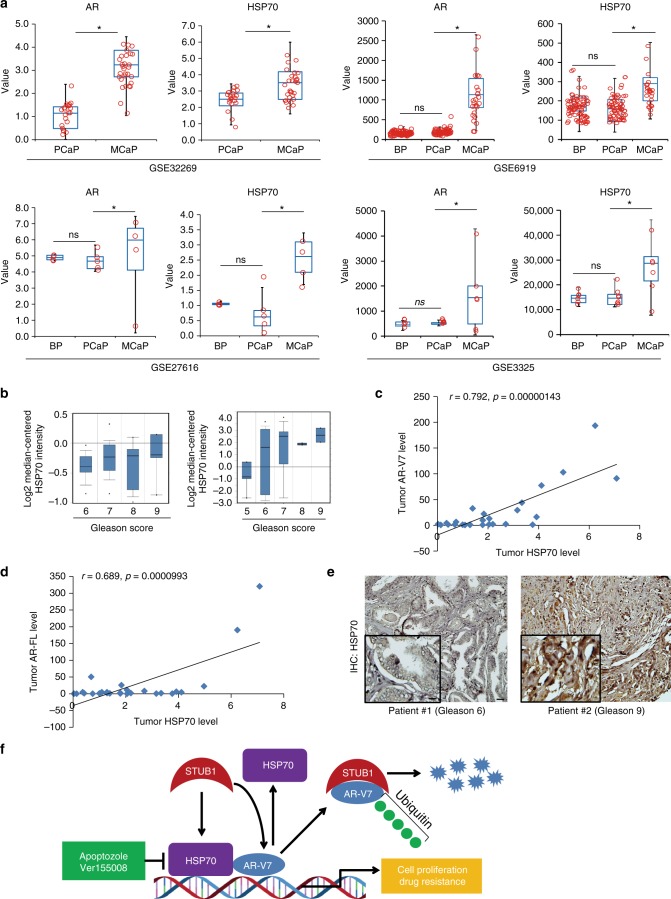
Fig. 7.
HSP70 level is correlated with AR/AR-V7 in prostate tumors. a In four independent GEO data bases (GSE32269, GSE6919, GSE27616, and GSE3325), AR and HSP70 gene expression levels were determined in benign prostate (BP), primary prostate cancer (PCaP), and metastatic prostate cancer (MCaP) tumor samples. *p < 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed Student’s t-test. b In two independent Oncomine databases, HSP70 gene expression was determined in different Gleason score prostate tumors. c, d Total RNA from 26 high Gleason score tumors was isolated and mRNA expression of AR-FL, AR-V7, and HSP70 was determined by qRT-PCR. The AR-FL/HSP70 correlation and AR-V7/HSP70 correlation were determined by Spearman rank correlation. The correlation coefficient was determined. e The prostate tumor biopsies from two prostate cancer patients (Gleason 6 and Gleason 9, respectively) were fixed and HSP70 immunohistochemistry staining of the tumor sections was determined. Scale bar 50 µm (outside) and 20 µm (inside). f Proposed pathway of HSP70/STUB1/AR-V7 complex in next generation anti-androgen resistance and prostate cancer progression. HSP70 forms complex with AR-V7 and increases AR-V7 transcriptional activity, STUB1 binds with HSP70 and disassociates HSP70 and AR-V7 binding, the ubiquitin ligase U-box domain of STUB1 binds with AR-V7 and promotes its ubiquitination and degradation. HSP70 inhibition by APO or VER promotes STUB1 and AR-V7 binding and ubiquitination