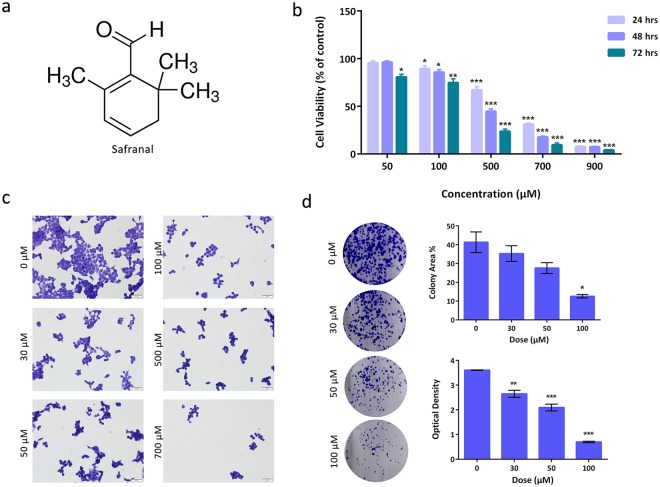
Figure 1.
Safranal inhibits growth and survival of HepG2 cells. (a) Chemical structure of safranal. (b) Cell viability of HepG2 cells after treatment with different concentrations of safranal for 24, 48 and 72 h. (c) Assessment of morphological changes of safranal-treated HepG2 cells (24 h). Cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet. (d) Representative images of colony formation assay of HepG2 cells treated with different concentrations of safranal (24 h). The effects of safranal treatment were quantified by calculating percent of area occupied by colonies in treated and non-treated samples (representative of triplicate samples) and absorbance of each treated and non-treated wells (representative of biological triplicates, each in technical triplicate). T-test was carried out (* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.001, ***p ≤ 0.0001).