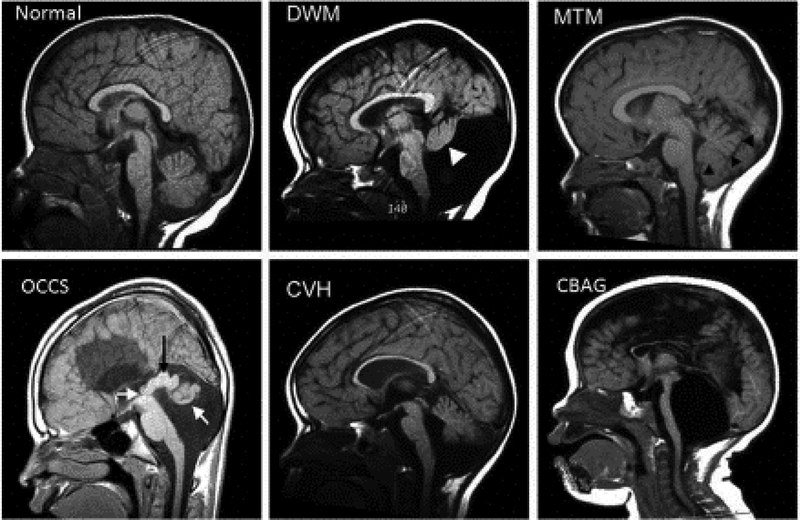
Figure 1: Examples of Human cerebellar malformations.
Mid sagittal MRI views of human cerebellar malformations with an unaffected individual shown for comparison. Dandy-Walker malformation (DWM) with white arrowhead highlighting the small cerebellar vermis rotated away from the brainstem in an enlarged posterior fossa encompassing a very large fourth ventricle. Molar Tooth Malformation (MTM) with black arrowheads marking the edge of the small vermis with cerebellar hemispheres occupying the residual space in a normally sized posterior fossa. Occulocerebrocutaneous syndrome (OCCS) with left white arrow indicating the third ventricle and black arrow highlighting a massively enlarged tectum; right white arrow points to rudimentary cerebellum. Also note lack of corpus callosum. Cerebellar vermis hypoplasia (CVH). Cerebellar agenesis (CBAG); note reduced size of pontine nucleus of the small brain stem.