Figure 4 -.
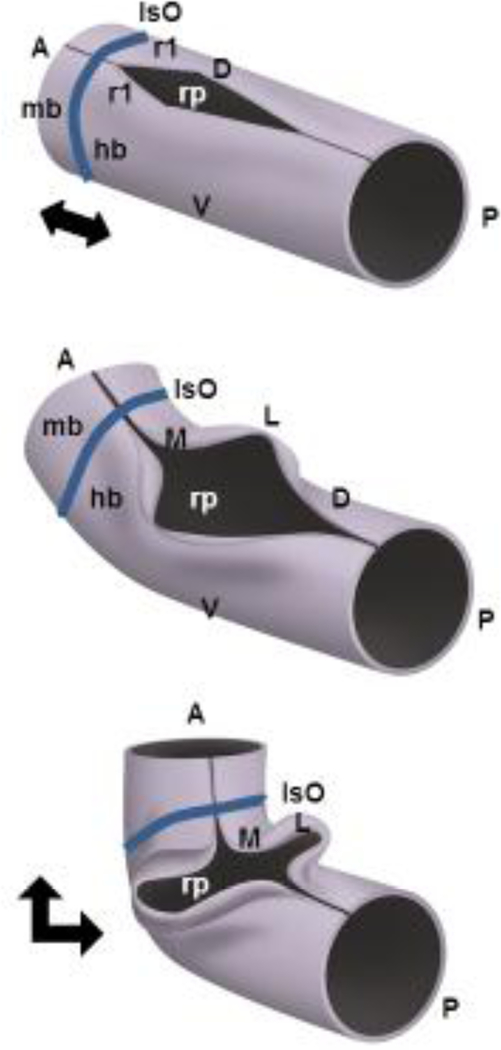
The cerebellum is a derivative of the anterior-most dorsal hindbrain, or dorsal (D) rhombomere 1 (r1). The establishment mid-hindbrain (mb-hb) boundary results in formation of a transient signaling center called the Isthmic Organizer (IsO), which secretes Fibroblast Growth Family 8 (FGF8) and WNT1 which are required for cell survival and pattern the adjacent tissue from e8–11.5 in mice. The developing cerebellar anlage undergoes a series of morphogenetic events between mouse embryonic (e) days 9 to e12.5 that rotate its anterior posterior (AP) axis by 90 degrees and convert it to the medio-lateral axis (ML) of the bilateral cerebellar wings. This reorientation is in large part driven by pontine flexure which converts the horizontal alignment of mid/hindbrain to nearly right angles (indicated by black double headed arrows). The roof plate (rp) is the single layer thick roof of the dorsal midline of the early neural tube which acts as another transient signaling center, expressing BMP and WNT secreted factors. The roof plate will eventually differentiate into the choroid plexus epithelium of the fourth ventricle. In rhombomere 1, roof plate derived Wnt expression is required to drive early cerebellar anlage ventricular zone proliferation, while secreted Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) gene expression is required to induce the cerebellar rhombic lip and correctly pattern expression of Pancreatic transcription factor (Ptf1a) in the ventricular zone of the nascent cerebellar anlage.