Figure 1. Three-dimensional (3D) homology structures and docking of vasotocin onto the modelled structures of the cV1aR and cV1bR.
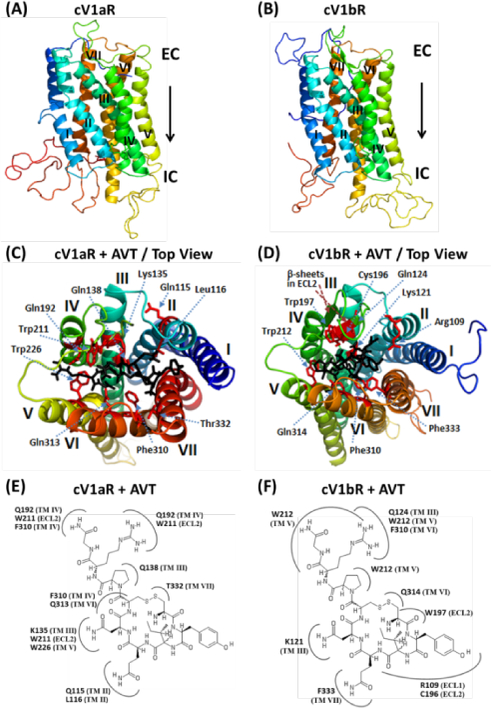
(A) and (B). Homology models of cV1aR and cV1bR built using the template opioid receptor (PDB ID: 4EA3). Seven transmembrane helices (TM-I-VII), each shown with a different spectral color are labelled with Roman numbers. EC – Extracellular side and IC – intracellular side of the receptor. (C) and (D). Top views of the binding amino acid residues (shown as sticks: magenta) of the modelled cV1aR and cV1bR structures with vasotocin (black). The residues are numbered according to their position in the primary sequence of the cV1aR and cV1bR (see Fig 3). The seven TM helices are labelled in different colors. Two-dimensional schematic views showing interactions of AVT and amino acid residues of the cV1aR and cV1bR structural models (E, F). All of the residues potentially interacting with the different parts of AVT are shown. Numbering of the residues and of the each TM is equivalent to that used in Fig 3. ECL- extracellular loop.
