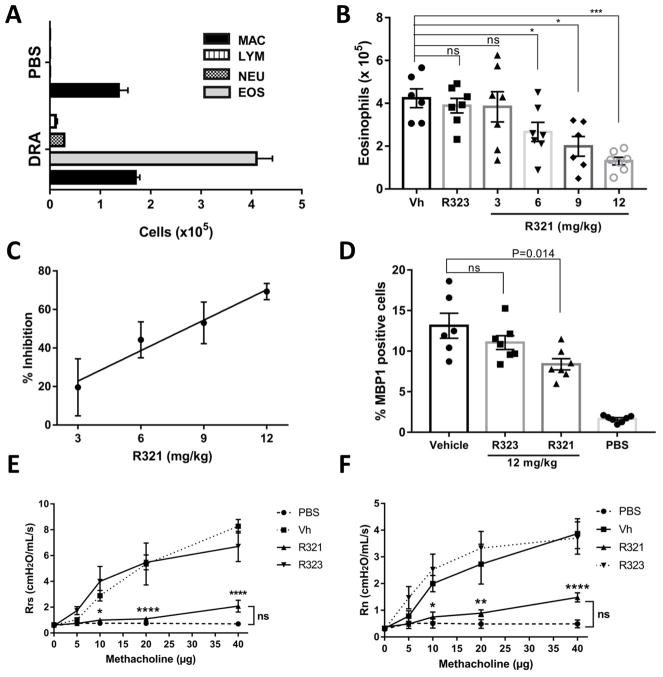
Figure 6. Prophylactic treatment with R321 significantly reduces eosinophil recruitment into the lung airspaces.
(A) The DRA-allergen challenge induces a robust eosinophilic response in female BALB/cJ mice as demonstrated by increased numbers of eosinophils in the BAL fluid. (B) Total eosinophil cell numbers (x10 ) in the BAL fluid show that R321 significantly inhibits eosinophil recruitment into the lung airspaces starting at an iv dose of 6 mg/kg. (C) The inhibitory effect of R321 is dose-dependent and reaches 69.33 ± 4.20% inhibition at 12 mg/kg. (D) Lungs were stained with anti-mMBP1 antibody to identify eosinophils. R321 (12 mg/kg) treatment reduces lung tissue eosinophil counts by 36.20 ± 5.28%. Results are displayed as % of mMBP1 positive cells as compared to total nucleated cells. The mean ± SEM are shown for 6–7 mice/treatment group from 3 independent experiments. R321 at 12 mg/kg significantly lowers respiratory system (E) and airway (F) responsiveness to methacholine as compared to vehicle or R323 controls. There is no significant difference between R321 treated and sham-challenged mice (n=5, except PBS group where n=4). (****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001,**p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns not significant).