Figure 2. The CRC consensus molecular subtyping system.
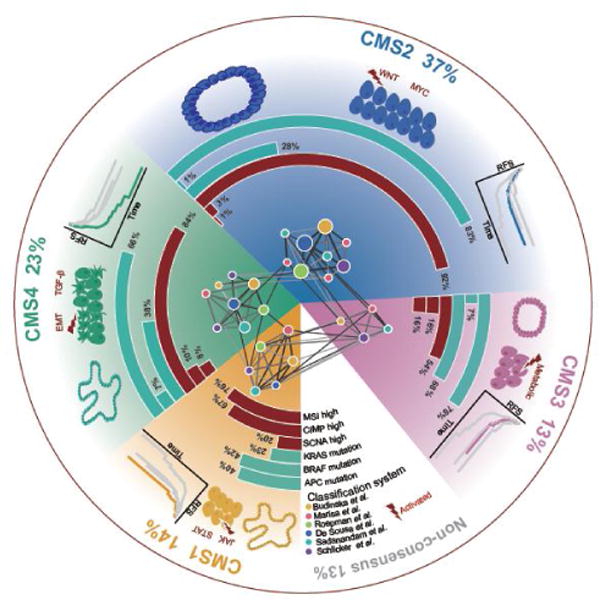
Network-based meta-analysis on six representative classification systems identified four consensus molecular subtypes of CRC. Each subtype shows distinct molecular characteristics and clinical associations. CMS1 (MSI Immune) tumors are characterized by CIMP high status, BRAF V600E mutations, diffuse immune infiltration, and are associated with worse survival after relapse. CMS2 (canonical) tumors are characterized by high somatic copy number alterations (SCNAs), overrepresented APC mutations and activated WNT and MYC signaling pathways. CMS3 (metabolic) tumors are largely CIMP low, enriched for KRAS mutations, and characterized by deregulation of metabolic pathways. CMS4 (mesenchymal) tumors display a high level of SCNAs, and are characterized by upregulation of EMT, TGF-β activation, stromal infiltration and worse relapse-free and overall survival. CMS2 and CMS3 tumors are more likely to be developed from tubular adenomas, while CMS1 and CMS4 tumors are potentially derived from serrated adenomas [142].
