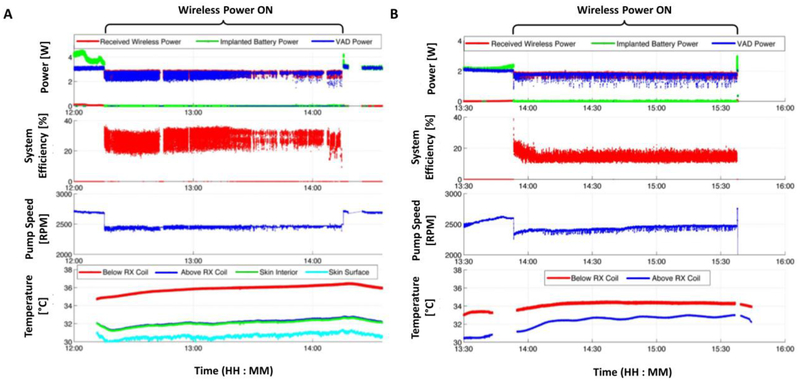
Figure 5. In-vivo FREE-D system performance measurements for short- and long-range configuration.
For both experiments, the adaptive tuning techniques allow for the system to maintain seamless wireless power delivery, without any backup battery assist. The VAD power and system efficiency fluctuations were attributed to systolic and diastolic cycles or expansions and contractions of the animals’ chest while they breathe. Measurements of wireless power delivered to the receiver, backup battery power, load power, pump speed, wireless power transfer efficiency, and temperature rise during (A) short- and (B) long- range configuration in-vivo experiment.