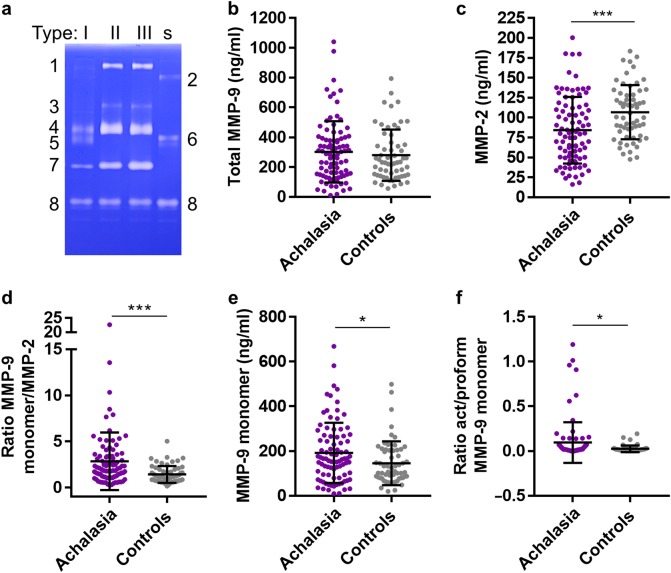
Fig. 1. Quantitative gelatin zymography analysis of achalasia patient sera.
Serum samples from patients with achalasia (n = 88) and controls (n = 60) were spiked with a known amount of a recombinant deletion mutant of human gelatinase B, pre-purified by gelatin-Sepharose affinity chromatography and subjected to zymography analysis. a Key for the interpretation of the gelatin-zymolysis. On top the type of achalasia patients from whom sera were analyzed are indicated, whereas the letter s indicates the standard sample with three recombinant human gelatinase B/MMP-9 forms. At the left side the numbers indicate gelatinase forms as follows: 1 = trimer form of MMP-9; 3 = covalent complex between MMP-9 and neutrophil gelatinase B-associated lipocalin (NGAL); 4 = proform of MMP-9; 5 = activated form of MMP-9; 7 = gelatinase A/MMP-2; 8 = recombinant deletion mutant spiked into each sample. At the right side a standard mixture of recombinant molecules is included as follows: 2 = recombinant trimer MMP-9; 6 = recombinant monomer proMMP-9; 8 = recombinant mutant of human MMP-9 with deletion of the O-glycosylated and hemopexin domains. b Total MMP-9 levels in achalasia versus control sera. c Levels of MMP-2 in achalasia versus control. d Ratios of MMP-9 monomers and MMP-2 in the comparisons of sera from achalasia patients and controls. e Levels of monomer proMMP-9 in achalasia versus control sera. f Ratios of monomeric activated MMP-9 and proMMP-9 in the comparisons of achalasia and control sera. For all cohorts the mean levels ±SD are provided, *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001. Achalasia: n = 88. Controls: n = 60