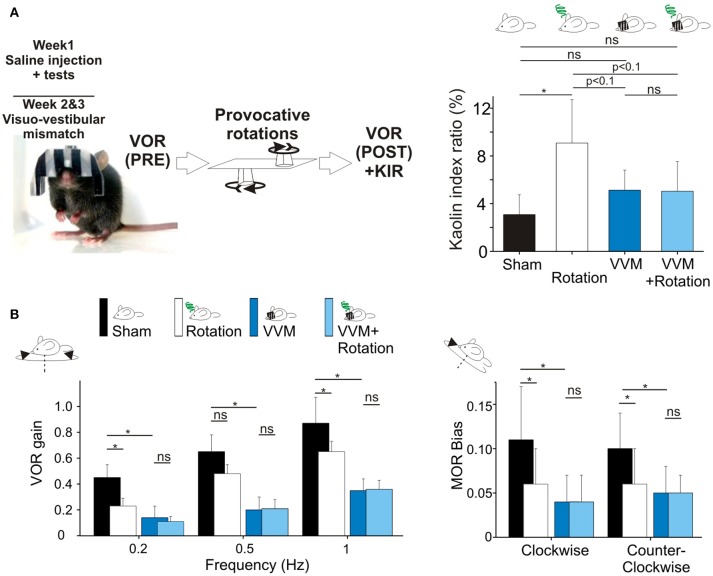
Figure 3.
(A) Visuo-vestibular mismatch reduces vestibular sensitivity. Left, picture of a mouse during the visuo-vestibular conflict protocol. The helmet is kept for 2 weeks. Right panel, Pica behavior demonstrated the protective effect of VVM protocol against MS induced by the double-rotation (B). Left panels, plots of angular VOR of the n = 8 mice before the provocative rotations (black and deep blue bars) and after the provocative rotations (white and light blue bars). Right panels, MOR bias ratios in the same conditions. No additional reduction of vestibular sensitivity was induced by the rotation, suggesting protective effects of the VVM protocol. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences with Holm-Bonferroni correction, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 respectively.