Figure 4.
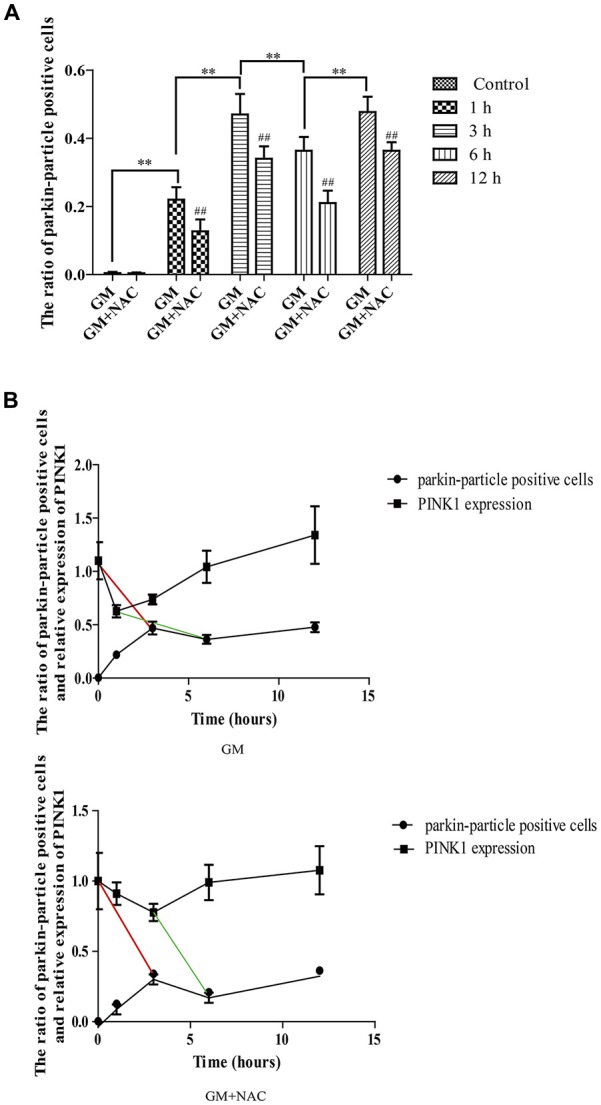
The ratio of parkin-particle positive cells changed following the function of PINK1. (A) The ratio of parkin-particle positive cells increased significantly in response to GM exposure for 1 h compared with control group which had almost no parkin particles. The ratio risen to the peak at 3 h then lessened at 6 h, followed by an increase again at 12 h. NAC co-treatment could alleviated the changes of the ratio of parkin-particle positive cells treated by GM. ##p < 0.01 vs. corresponding GM groups, **p < 0.01, results were shown as mean ± SEM. (B) We also compared the changes of PINK1 expression and the ratio of parkin-particle positive cells after GM stimulus and NAC co-treatment. Results showed the delayed peaks (red line segments) and valleys (green line segments) of parkin-particle positive cells in contrast with PINK1 expression. NAC co-treatment could mitigate the changes of both PINK1 expression and the ratio of parkin-particle positive cells after GM exposure.
