Figure 5.
Coordination of Metabolic Pathways across Cellular Compartments Depends on Substrate and Macrophage Polarization State
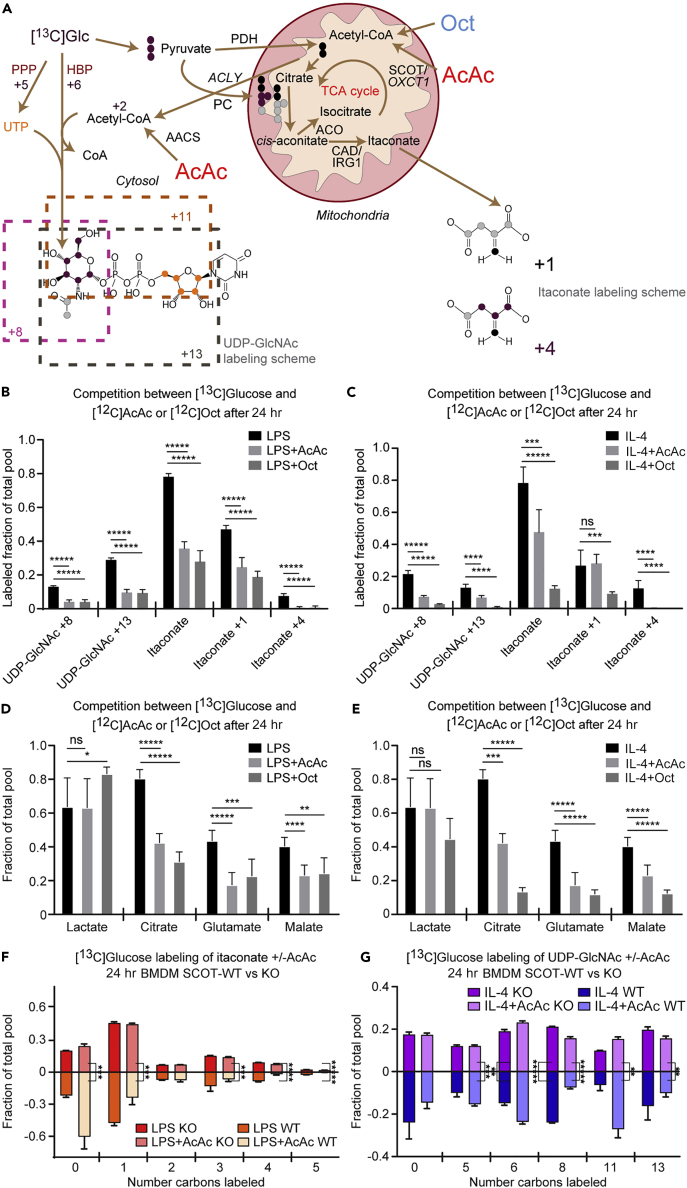
(A–G) (A) Labeling map depicting integration of mitochondrial ketone body AcAc metabolism with UDP-GlcNAc and itaconate biosynthesis. Competition between 10 mM [U-13C6]glucose-derived labeling with unlabeled 1 mM AcAc or 0.5 mM octanoate (Oct) among (B and C) individual UDP-GlcNAc or itaconate isotopologues (n > 6/group) or (D and E) total labeled pools of representative TCA cycle intermediates (a subset of data shown in E also were utilized in Puchalska et al. (2018)) (n > 6/group) in (B and D) LPS-polarized (25 ng/mL) or (C and E) IL-4-polarized (25 ng/mL) wild-type (WT) bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) after 24 hr of exposure. Competition between 10 mM [U-13C6]glucose-derived labeling and 1 mM unlabeled AcAc of (F) itaconate or (G) UDP-GlcNAc in (F) LPS- or (G) IL-4-polarized WT or SCOT KO BMDMs after 24 hr of exposure (n = 4/group; a portion of the BMDM WT data utilized from Figures 5B and 5C). ACLY, ATP citrate lyase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; ACO, aconitate hydratase; CAD, cis-aconitate decarboxylase; AACS, acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase; SCOT, succinyl-CoA:oxoacid A transferase. Data expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Significant differences determined by multiple Student's t test with Holm-Sidak correction when compared with control. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, *****p < 0.00001, as indicated.