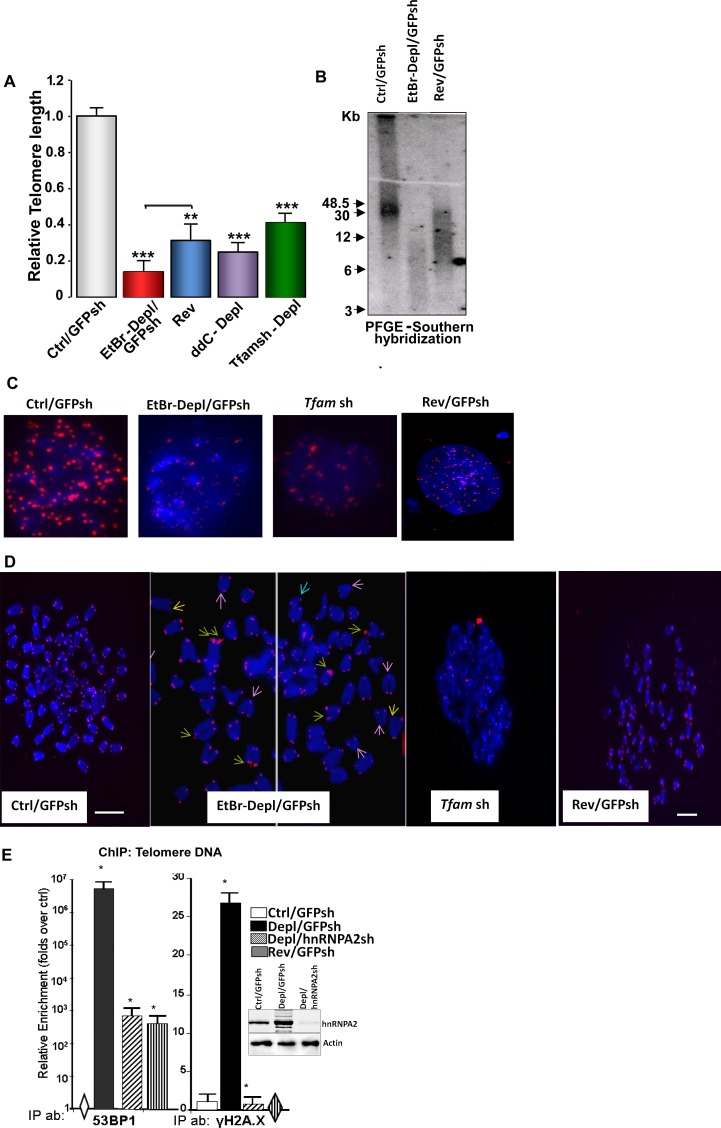
Fig 1. Partial mtDNA depletion-induced telomere length attrition in immortalized C2C12 cells.
(A) Relative Telomere length analysis using genomic DNA isolated from control, mtDNA-depleted (EtBr treated, 2,3’-ddC treated or Tfam shRNA as indicated in the figure) and reverted cells. Real Time PCR was performed using primers specific for telomere DNA and normalized using control DNA (36B4.Primer sequences are provided under Materials and Methods; (B) PFGE of total DNA from control, mtDNA-depleted, and reverted cells followed by in-gel hybridization using a 32P-labeled telomere DNA-specific probe. (C) Q-FISH on nuclei of control, MtDNA-depleted (EtBr or Tfam sh) and reverted cells. Telomeres are probed with Cy3-PNA (red) and nucleus stained with DAPI (blue). The width of each field shown is 15 μm. (D) Representative image of Q-FISH of telomere Cy3-PNA probe (Red) on metaphase spreads (Blue) in Control, mtDNA depleted (EtBr or Tfam sh) and reverted cells. Fragile telomeres (green arrows), signal-free ends (yellow arrows) and chromosome end fusions (pink arrows) are indicated in cells depleted of mtDNA. Chromosomes were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 15 μm for all panels. (E) DNA Damage Response Activated in MtDNA depleted cells. Recruitment of DNA damage response factors at the telomere DNA assessed by ChIP analysis in control, MtDNA-depleted, MtDNA-depl/hnRNPA2sh and reverted C2C12 cells. Immunoprecipitations were performed using antibodies to DNA damage response factors, 53BP1, and phosphorylated H2A.X. Western Immunoblot in control, mtDNA depleted and mtDNA-depleted/hnRNPA2sh cells shows the efficiency of hnRNPA2 shRNA.