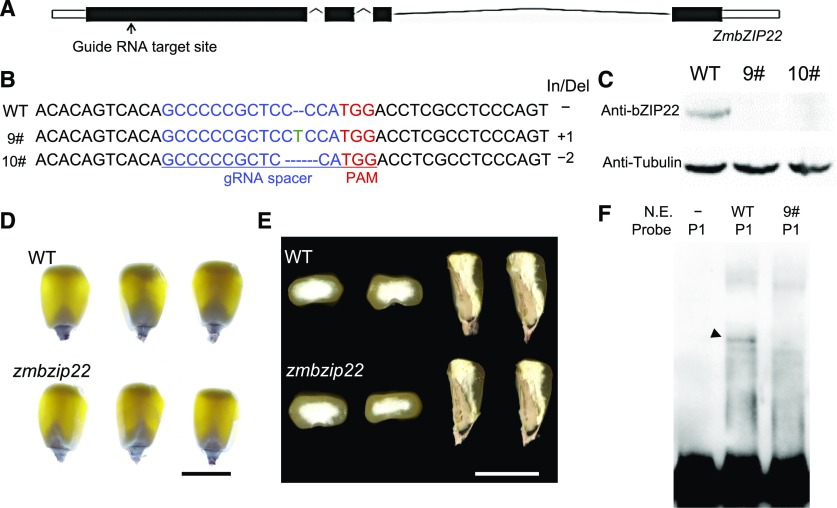
Figure 4.
CRISPR-Cas9-Based Mutation of ZmbZIP22 and Phenotype Analysis of zmbzip22.
(A) Schematic representation of the gene model of ZmbZIP22. The arrow indicates the gRNA target site.
(B) The DNA sequences of the Cas9-edited ZmbZIP22 gene. The 20-bp guide RNA (gRNA) spacer sequence for the Cas9/gRNA complex is shown in blue, and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) site is shown in red. Deleted nucleotides are depicted as dashes, and inserted nucleotides are shown in green. The lengths of the insertions and/or deletions (In/Del) are shown. 9#, zmbzip22-mu9; 10#, zmbzip22-mu10.
(C) Protein gel blot analysis of ZmbZIP22 showing the absence of ZmbZIP22 in zmbzip22-mu9 and zmbzip22-mu10. Antitubulin antibody was used as the internal control. Total proteins were extracted from whole kernels at 15 DAP.
(D) Light transmission analysis of wild-type (WT) and zmbzip22 mature kernels. The homozygous mutant kernels and homozygous wild-type kernels were randomly selected from a segregating F2 population, genotyped and viewed on a light box. Bar = 1 cm.
(E) Transverse and sagittal sections of wild-type and zmbzip22 mature kernels. The homozygous mutant kernels and homozygous wild-type kernels were randomly selected from a segregating F2 population. Bar = 1 cm.
(F) EMSA of wild-type and zmbzip22-mu9 nuclear extract with Probe 1. Arrowhead points to the nuclear extract-induced shifted band. P1, Probe1; N.E., nuclear extract.