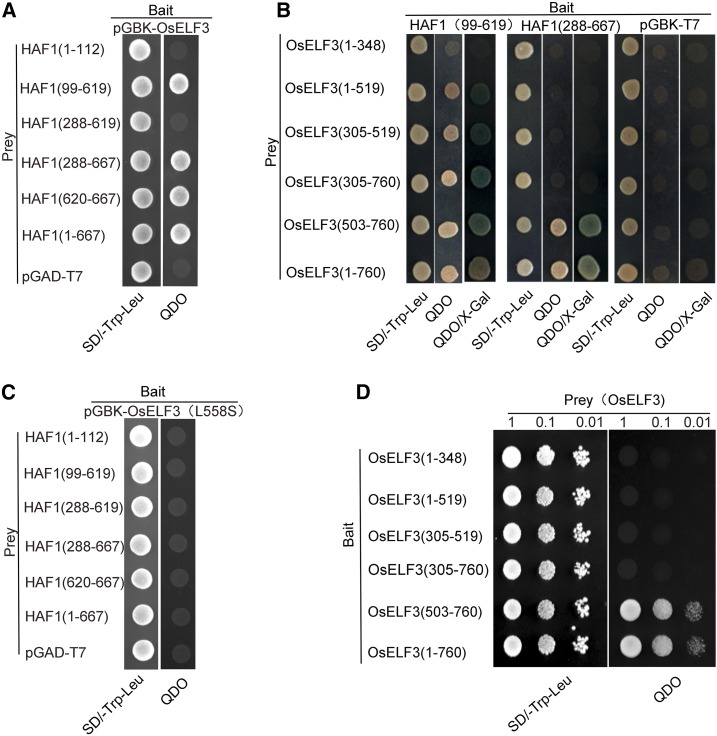
Figure 1.
Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay of Interactions between OsELF3 and HAF1.
(A) Interaction analysis of OsELF3 (as bait) with prey constructs containing HAF1 truncated fragments.
(B) Interaction analysis between a series of truncated OsELF3 and HAF1 fragments. HAF1 fragments (amino acids 99–619 or 288–667) interact most strongly with the C-terminal domain of OsELF3 (amino acids 503–760).
(C) The substitution of leucine to serine (L558S) in OsELF3 abolishes its interaction with HAF1.
(D) The C-terminal domain of OsELF3 (amino acids 503–760) is essential for its homodimer formation. Empty pGBK (bait) and pGAD (prey) were used as negative controls. Blue clones in the X-Gal assay and clones that grow on QDO medium indicate protein interactions in the yeast cells. QDO indicates SD-Trp-Leu-His-Ade medium.