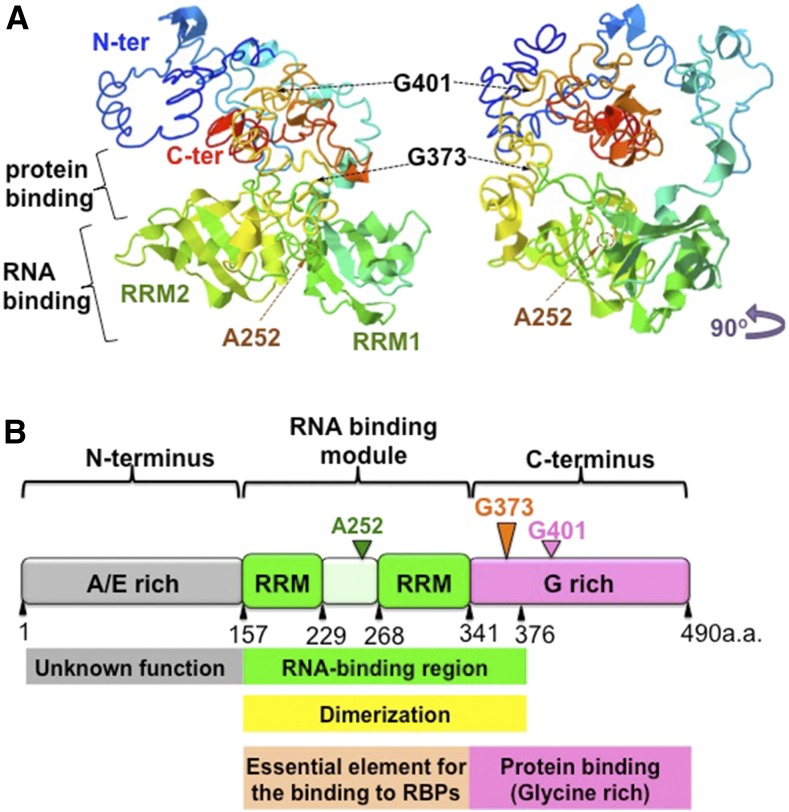
Figure 14.
Hypothetical Function and Structure of the Multiple Domains of RBP-P.
(A) Predicted structure of RBP-P. Right panel is a 90° left rotation view of the left panel. The two RRM motifs, RRM1 and RRM2, are labeled. The residues Gly-401, Gly-373, and Ala-252 are indicated by arrows.
(B) Schematic representation of the structure and function of the RRM domain and the N and C terminus in RBP-P. The N terminus of RBP-P contains the Ala-rich and Glu-rich motifs of unknown function. The RNA binding module consists of two RRM domains, ∼80 amino acids in length, the interdomain linker, and a short sequence in the C terminus. This protein module is responsible for RNA binding activity as well as dimerization with another RBP-P molecule or other proteins, such as RBP-L. The glycine-rich C terminus is involved in protein-protein interactions.