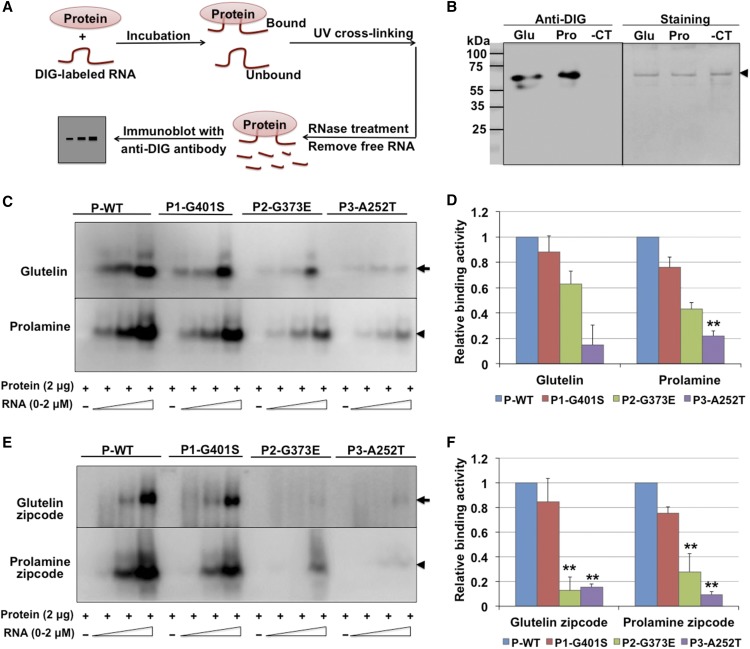
Figure 5.
In Vitro Binding Activities of Wild-Type and Mutant RBP-P to Glutelin and Prolamine mRNAs.
(A) Simplified representation of the RNA-protein UV-cross-linking assay.
(B) Binding activity of wild-type RBP-P to glutelin (Glu) and prolamine (Pro) mRNAs compared with the negative RNA control (-CT, RNA transcribed from cloning vector). Left panel: Immunoblot with anti-DIG antibody to detect the bound RNAs. Right panel: Coomassie blue-stained gel to show cross-linked RBP-P. Arrowhead indicates the position of RBP-P protein on SDS-PAGE gel.
(C) and (E) Binding activities of wild type (P-WT) and mutant RBP-P lines (P1-G401S, P2-G373E, and P3-A252T) to full-length glutelin and prolamine RNAs (C) and zip code (E) sequences. Arrow and arrowheads in indicate the mobility of glutelin and prolamine RNA bound RBP-P, respectively.
(D) and (F) Relative binding affinities of mutant RBP-Ps to glutelin and prolamine RNAs full-length (D) and zip code (F) sequences compared with wild-type RBP-P as assessed by ImageJ analysis of immunoblot results depicted in (C) and (E). The results represent the means ± se of duplicate determinations. *P value of two-tailed t test < 0.05; **P value of two-tailed t test < 0.01.