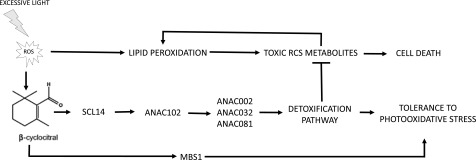
Figure 13.
β-cc Mediates Resilience to Photooxidative Stress via the SCL14-Dependent Xenobiotic Response.
Photooxidation under excessive light stress generates toxic RCS metabolites and increases β-cc concentration. β-cc induces the expression of SCL14 leading to enhanced expression of ANAC102 and finally a strong activation of the xenobiotic detoxification response. In this response, ANAC102 is upstream of ANAC002, ANAC032, and ANAC081 expression and consequently of the enzymes controlled by these transcription factors. Furthermore, the strong induction of the AER, AKR, ALDH, and SDR enzymes and of the glucosyl and glutathione transferases in the xenobiotic detoxification pathway assures the elimination of the RCS produced under stress conditions. Reducing RCS accumulation limits the positive feedback on lipid peroxidation and leads to tolerance rather than cell death.