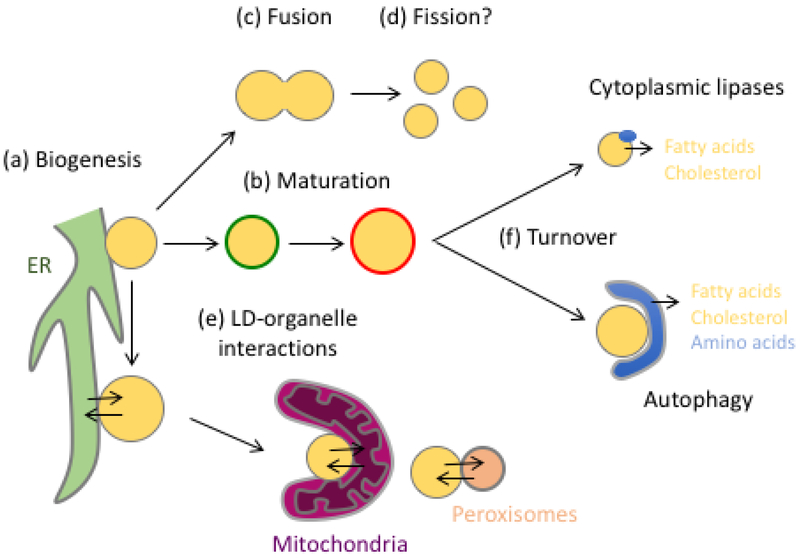
Figure 1: The LD Lifecycle.
LDs undergo a complex lifecycle that begins with biogenesis from the ER (a). LDs undergo a maturation process involving the sequential recruitment of different proteins, such as perilipins (b); the change from green to red indicates the sequential recruitment of proteins. Under certain conditions LDs may undergo fusion (c) or fission (d), and LDs may make contacts with a number of other organelles, including the ER, mitochondria, and peroxisomes (e). Arrows indicate lipid and/or protein transfer between organelles, although in many cases the types of lipid being transferred and direction of transfer are as yet unknown. Finally, LDs can be turned over via lipolysis involving cytoplasmic lipases, or via macroautophagy, referred to as lipophagy (f).