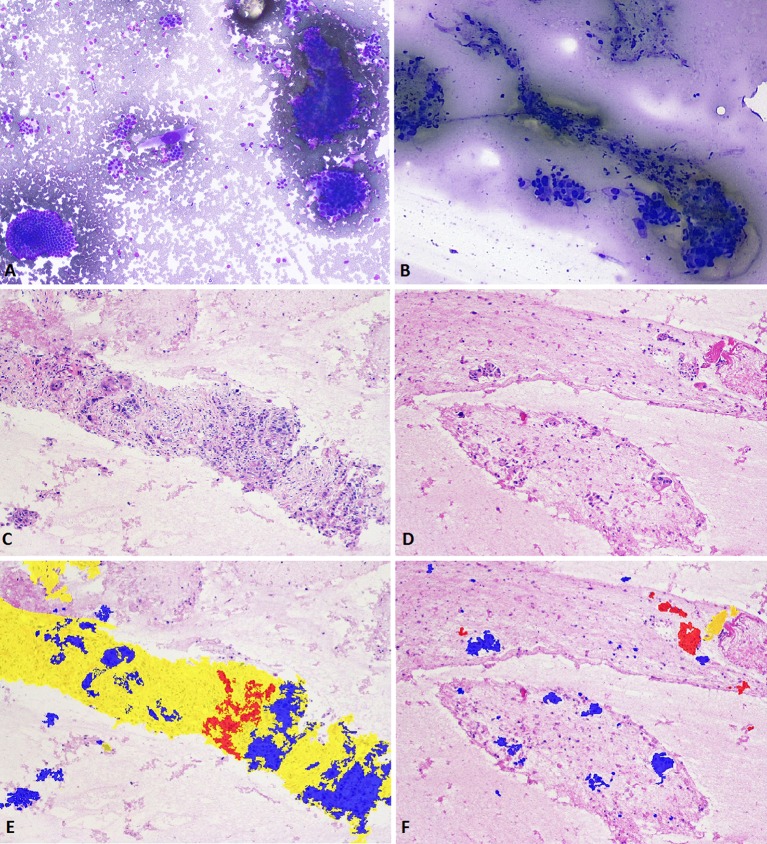
Figure 3.
Rapid onsite evaluation of a pancreatic head mass biopsied using the Franseen needle reveals a cellular specimen comprising malignant cells, fibrosis and benign reactive ductal epithelium (A; Diff-Quik staining, 200×). The corresponding aspirate from a standard FNA needle reveals scattered malignant cells and with minimal fibrosis (B; Diff-Quik staining, 100×). H&E staining of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (100×) procured with the Franseen needle. Cores of exuberant dense desmoplastic fibrosis are seen entrapping malignant ductal epithelium and scattered benign residual acini on sections from the cell block (C). The corresponding image of a specimen from an FNA needle reveals minimal tumour cells and lack of any desmoplastic fibrosis (D). Digital image analysis reveals dense desmoplastic fibrosis (highlighted yellow) surrounding malignant (highlighted blue) ductal groups and foci of residual benign acini (E). The corresponding image of a specimen from an FNA needle reveals fewer tumour cells, lack of any significant architecture and a minute fragment of fibrosis (F). FNA, fine needle aspiration.