Figure 2.
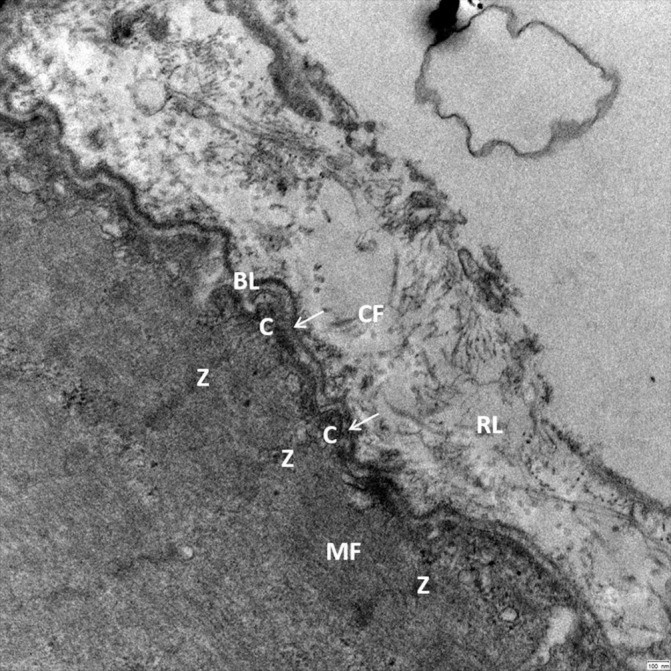
Transmission electron microscopy reveals the close cell–ECM interaction in human skeletal muscle (musculus vastus lateralis, 25 000× magnification) allowing a bidirectional cell–ECM interaction. Myofilaments (MF) are connected by Z-lines (Z) and costameres (C) to the adjacent basal lamina (BL) and the surrounding reticular lamina (RL). Crossbridging structures (arrows) connect the Z-lines and costameres to the dense part of the basal lamina. The reticular lamina is structured by a network of collagen fibrils (CF) and additional ECM molecules, which have a close connection to the basal lamina allowing bidirectional transmission of mechanical forces. ECM, extracellular matrix.
