Figure 7. Model of the Cas6-RT Domain Interaction in MMB-1 Cas6-RT-Cas1.
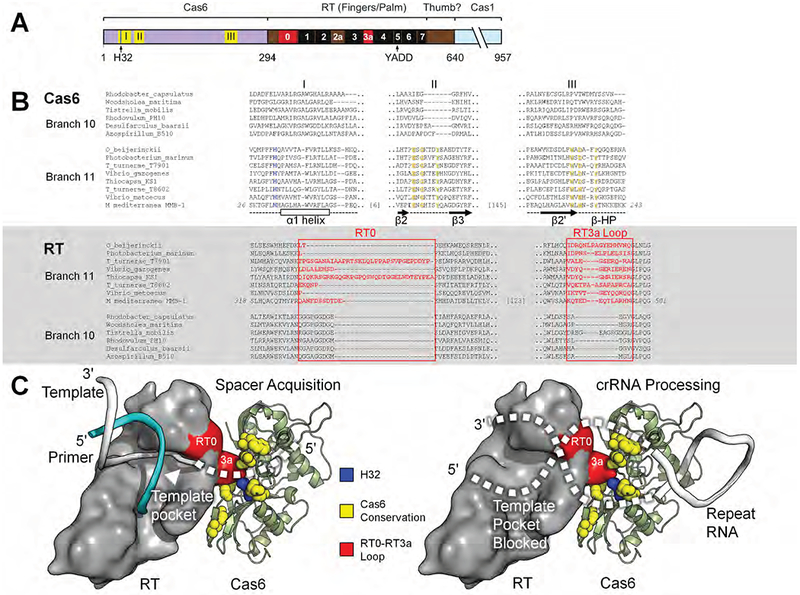
(A) Schematic of the Cas6-RT-Cas1 fusion protein. Yellow (I, II, III) and red (RT0, RT3a) show the location of sequences aligned in panel B; black boxes indicate conserved RT sequence blocks. The location of the conserved H32 residue in motif I is indicated by a blue line. (B) Branch-specific sequence features of Cas6 (top) and RT (bottom) shown in representative alignments from branches 10 and 11. In the Cas6 alignment, H32 is in blue, and additional conserved residues characteristic of Branch 11 are in yellow. Secondary structure elements are indicated below the Cas6 alignment. In the RT alignment, RT0 and RT3a are in red. (C) Model of the potential Cas6-RT domain interaction. The branch-specific RT0-RT3a loop surface (red) is positioned near the branch-specific Cas6 conserved motifs (yellow), including highly conserved H32 (blue). During spacer acquisition, left, the template strand is unobstructed from the template pocket, whereas during crRNA processing, right, the bound CRISPR repeat RNA may sterically block or enter the template pocket unproductively. The RT domain surface is loosely based on a group II intron RT structure in complex with template-primer (PDB: 6AR1; template, white; primer, cyan) and manually docked against MMB-1 Cas6. Features and amino acid residues are colored as in (B).
