Figure 3: Data integration.
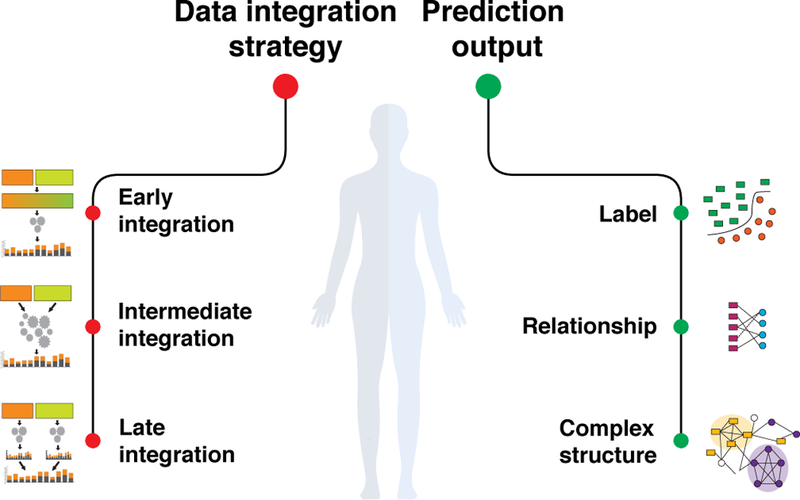
Data integration approaches combine multiples sources of information in a statistically meaningful way to provide a comprehensive analysis of a biomedical point of interest. Broadly, existing approaches employ three distinct modeling strategies (i.e., early, intermediate, and late integration; see also Figure 2) and produce three types of prediction outputs (i.e., a label representing probability of an entity belonging to a given class; a relationship representing probability of an association between two entities; and a complex structure, such as an inferred network or a partitioning of entities into groups).
