Fig 1. Pro-σK resides in a membrane complex with the B protease in a IVB-dependent manner.
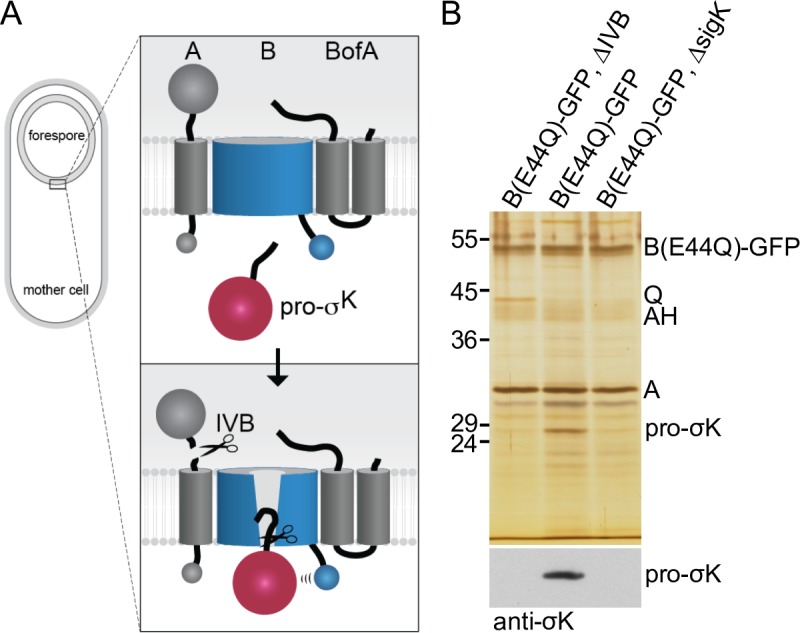
(A) Schematic model of regulated intramembrane proteolysis during sporulation. Prior to forespore signaling, A and BofA hold B in a closed conformation in the membranes surrounding the forespore. IVB-dependent cleavage of A triggers a conformational change in B allowing pro-σK access to the catalytic center of the protease. Pro-σK processing then leads to late mother cell gene expression and spore maturation (not depicted in the diagram). For simplicity, A and BofA are shown interacting with B but not each other. Co-immunoprecipitation and cytological assays [33] suggest A and BofA interact in the absence of B. (B) Silver-stained gel of immunoprecipitated proteins from detergent-solubilized membrane preparations of the indicated strains at hour 4 of sporulation. Proteins indicated on the right were identified by mass spec or from immunoprecipitations using mutant strains. Immunoblot of the same samples using anti-σK antibodies is shown below.
