Figure 2.
Predicted Resistance Mutations
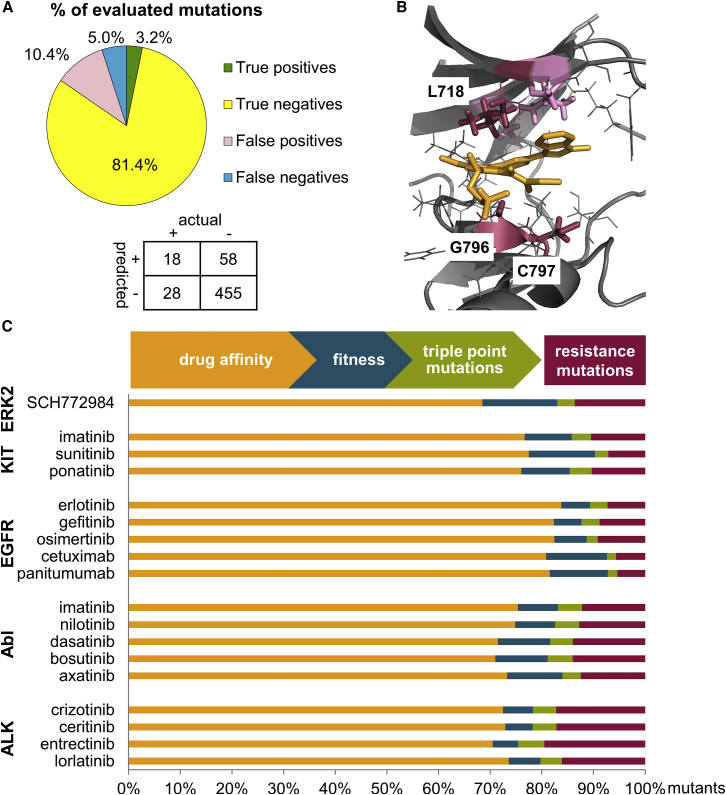
(A) Performance of the workflow on ERK2-SCH772984. The confusion matrix shows the absolute number of mutations (+, resistant; −, sensitive).
(B) Predicted resistance hotspots that are consistent with clinically observed resistant mutants for the representative case study EGFR (gray) and osimertinib (orange), PDB: 4ZAU (Yosaatmadja et al., 2015). Residues within 5 Å of the ligand are depicted in gray, predicted and clinically observed resistance hotspots are highlighted as crimson sticks and labeled, predicted hotspot residues that have not yet been observed in the clinic are shown as pink sticks; figure created with PyMOL (PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.7, Schrödinger, LLC).
(C) Contribution of filtering steps to the identification of resistance mutations. The majority of mutants were discarded because they did not decrease drug affinity in comparison with binding of the endogenous ligand (orange). Mutations were further removed because of abrogated clonal fitness (blue) or because they required triple codon changes to be formed (green). The remaining pool of mutations (crimson) is predicted likely to confer resistance to drug treatment.