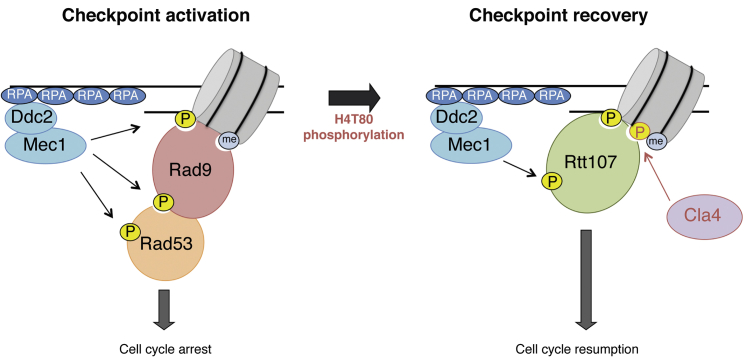
Figure 7.
Model of DNA Damage Checkpoint Recovery Initiation
Schematic model depicting the role of H4T80ph in the transition from checkpoint activation to checkpoint recovery. In response to genotoxic stress, Rad9 recruitment to sites of DNA damage, via interaction with H3K79me and γH2A, drives DDC activation. Cla4-dependent H4T80 phosphorylation triggers DDC recovery by recruiting Rtt107, which displaces Rad9 from H3K79me and γH2A, thereby interrupting the signaling cascade.