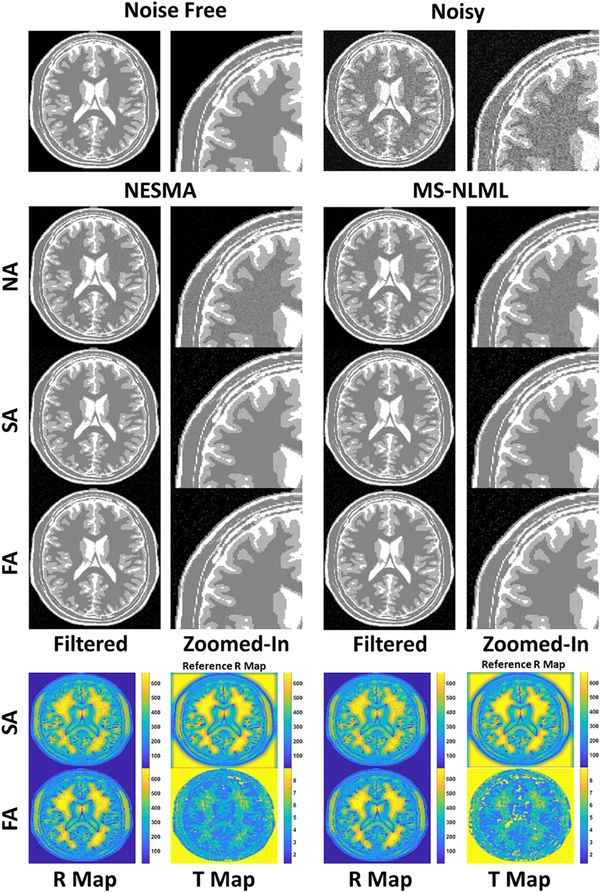
Figure 1.
Filtering performance of non-adaptive (NA), semi-adaptive (SA), and fully-adaptive (FA) NESMA and MS-NLML filters on a synthetic T2W dataset generated with SNR = 25. Results are shown for TE = 60 ms. The grayscale is consistent across all filtered and zoomed-in images. R-maps and T-maps show the respective values of the number of voxels and threshold selected at each location for the NESMA and MS-NLML filters. The reference R-map represents the optimal number of voxels selected at each point in the image. The filtered images demonstrate the nearly identical noise reduction and feature preservation of the NESMA filter as compared to the MSNLML filter for NA, SA, and FA methods. Further, both adaptive methods demonstrate superior noise reduction compared to their NA counterparts for both the NESMA and MS-NLML filters.