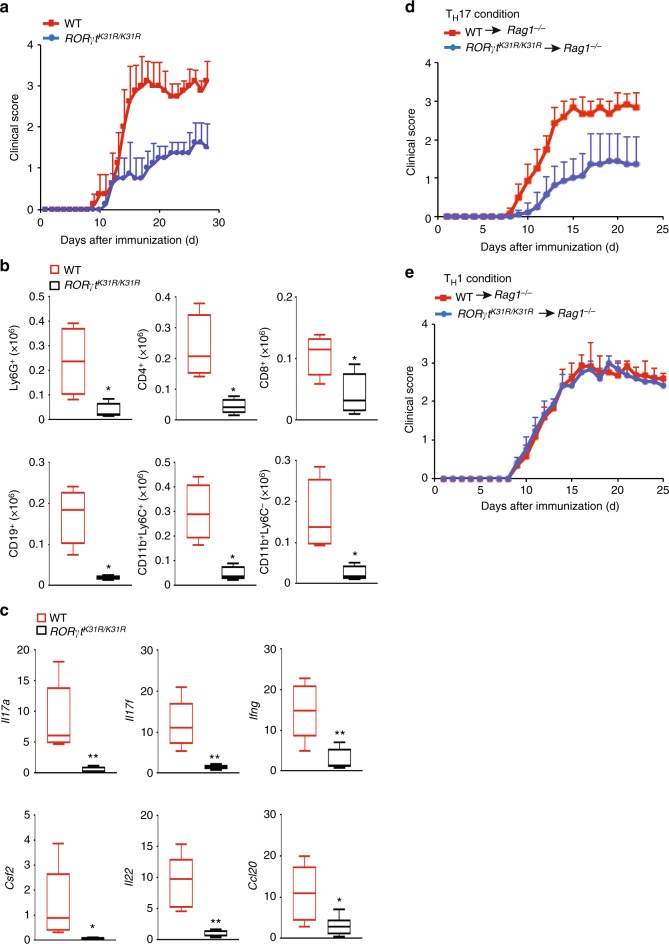
Fig. 5.
RORγtK31R/K31R mice are resistant to induction of EAE. a Mean clinical EAE scores of female WT and RORγtK31R/K31R mice (n = 10 per genotype) from days 0 to 30 after immunization with the EAE-inducing epitope MOG35-55. b Quantification of CNS-infiltrating cells from WT and RORγtK31R/K31R mice in which EAE was induced (same as in a) expressing characteristic mononuclear cell surface markers, assessed using flow cytometry at the peak of disease. c qPCR analysis of cytokine-encoding Il17a (top left), Il17f (top middle), Ifng (top right), Csf2 (bottom left), Il22 (bottom middle) and Ccl20 (bottom right) mRNA in the CNS-infiltrating lymphocytes assessed in a. Expression is presented relative to that of the control gene Actb. d Mean clinical EAE scores of female Rag1−/− mice reconstituted with CD4+ T cells from MOG35-55-primed WT or RORγtK31R/K31R mice (n = 5 per genotype) that were further expanded in vitro for 3 d in the presence of MOG35–55 and IL-23 (20 ng/ml) (TH17 conditions). e Mean clinical EAE scores of female Rag1−/− mice reconstituted with CD4+ T cells from MOG35–55-primed WT or RORγtK31R/K31R mice (n = 5 per genotype) that were further expanded in vitro for 3 d in the presence of MOG35-55 and IL-12 (20 ng/ml) (TH1 conditions). *P < 0.05 (t-test); **P < 0.01 (t-test). Data are from three experiments (b; c, presented as median [central line], maximum and minimum [box ends], and outliers [extended lines])