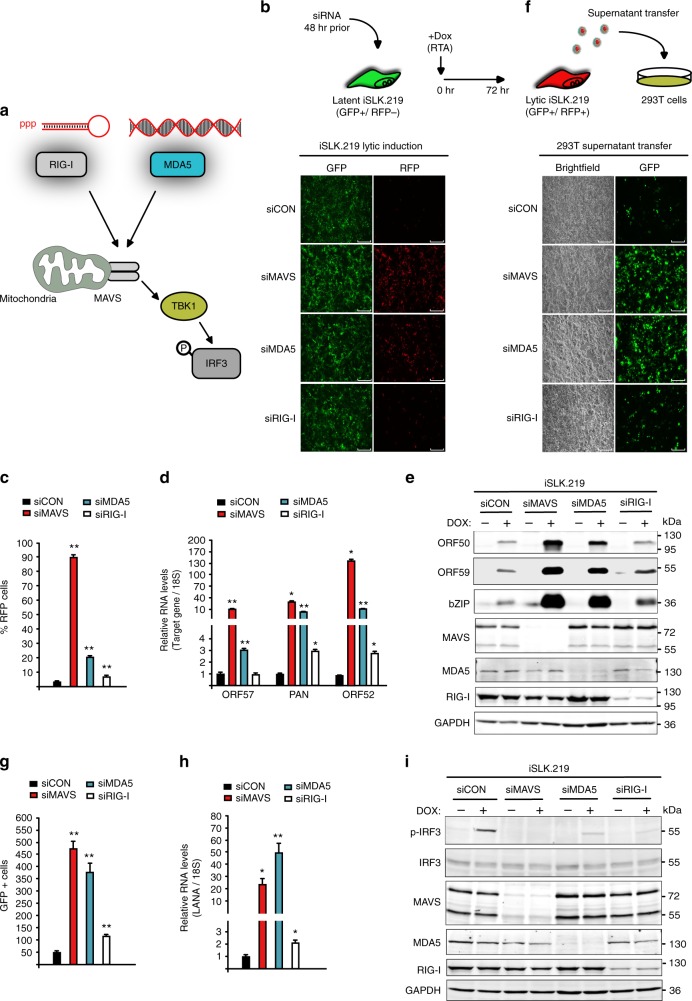
Fig. 1.
Knockdown of RLRs and MAVS enhances KSHV lytic reactivation in iSLK.219 cells. a Schematic of RLR-MAVS signaling pathway. b iSLK.219 cells were transfected with indicated siRNAs for 48 h and then treated with Dox for 72 h. GFP and RFP were imaged 48 h post-Dox treatment. Bar indicates 750 μm. c RFP positive cells were quantified by flow cytometry 48 h post-Dox treatment. d RNA extracted from iSLK.219 24 h post-reactivation and expression of the indicated genes was quantified by RT-qPCR. e Western blot analysis of cell lysate from latent and 48 h post-Dox treatment iSLK.219 cells described in (b). f HEK293T cells were infected with supernatants of reactivated iSLK.219. GFP images were captured 48 h postinfection. Bar indicates 300 μm. g Quantification of GFP positive cells in (f). h RNA was extracted from HEK293T cells in (f) and KSHV LANA gene expression was monitored by RT-qPCR. i Western blot analysis of cell lysates from latent and 24 h post-Dox treatment iSLK.219 cells in (b). Error bars in all panels represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments. p Values were determined by the Student’s t test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01