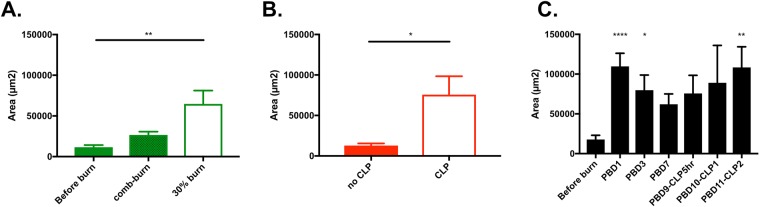
Figure 5.
cNETs levels increase after burn and sepsis. (A) Significantly more cNETs are trapped in the microfluidic device after small (comb burn) and large (30% TBSA) burns in rats at 1 PBD (N = 8–13 rats for each group). Data represents the area of trapped cNETs in the devices. Comparisons are performed using the Kruskal-Wallis test; **p ≤ 0.01. (B) Significantly more cNETs are trapped in the microfluidic device from blood of 30% TBSA rats, at 9 PBD and 6 hours after CLP compared to the no CLP (N = 5–8 rats for each group). Data were compared using Mann-Whitney test; *p ≤ 0.05. (C) The area of trapped cNETs in microfluidic devices surges at 1 PBD (N = 8–18 rats for each group). The trapped cNETs area decreases slowly in the days after the injury. The trapped cNETs area increases steadily during sepsis after cecal ligation puncture. Data at each timepoint were compared using Kruskal-Wallis test; *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ****p ≤ 0.0001.