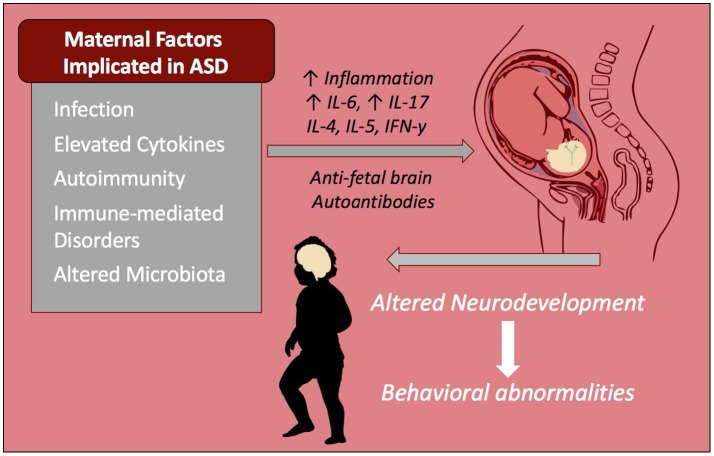
Figure 1.
Maternal immune influences during gestation increase risk of ASD. Infection and immune-mediated/autoimmune disorders in the mother are known risk factors that increase the chances of a child developing ASD. These inflammatory factors as well as altered maternal microbiota may be contributing to increased inflammatory cytokines and/or autoantibodies that react to fetal brain tissue. These factors alter the immune profile and neurodevelopment of the child and are linked to behavioral abnormalities seen in ASD including repetitive behaviors, stereotypies, anxiety, and impaired social behaviors.