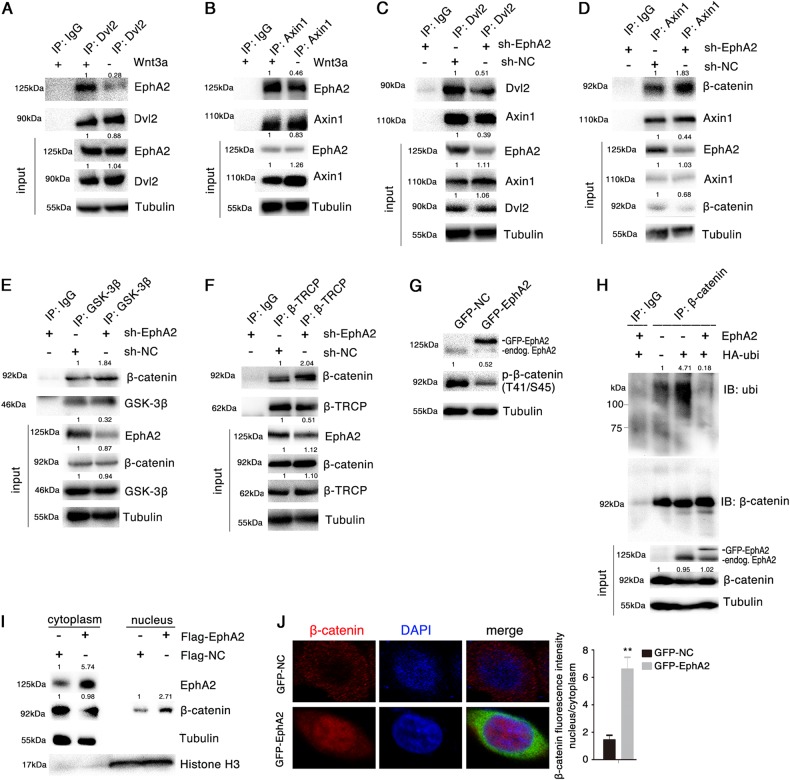
Fig. 3. EphA2 destabilizes the β-catenin destruction complex and promotes its nuclear accumulation.
a, b Interaction between endogenous EphA2 and Dvl2 (a) or Axin1 (b) with or without Wnt3a stimulation in AGS cells, assayed by co-IP. c–f Interaction between endogenous EphA2 and β-catenin destruction complex. A stable AGS cell line in which EphA2 expression was inhibited via EphA2-specific shRNA virus, and cell lysates were subjected to co-IP followed by Western blotting for indicated antibodies. g Phosphorylation of β-catenin at residues Thr41/Ser45 after transfection of AGS cells with GFP-EphA2 for 48 h. h Levels of β-catenin ubiquitination in AGS cells after transfection with the indicated expression vectors for 48 h followed by treatment with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 for 4 h before harvesting. β-catenin was immunoprecipitated with anti-β-catenin and subjected to Western blotting with anti-ubiquitin and anti-β-catenin. i Relative levels of β-catenin and EphA2 at 48 h post-transfection with EphA2 or negative control expression vectors in AGS cells assessed with Western blotting of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins. j Effect of EphA2 overexpression on the subcellular localization of β-catenin in AGS cells monitored by immunofluorescence. Relative accumulations of proteins in different groups compared with the negative control group are indicated. Significant differences were determined with the Student’s t-test. **P < 0.01 compared with control group