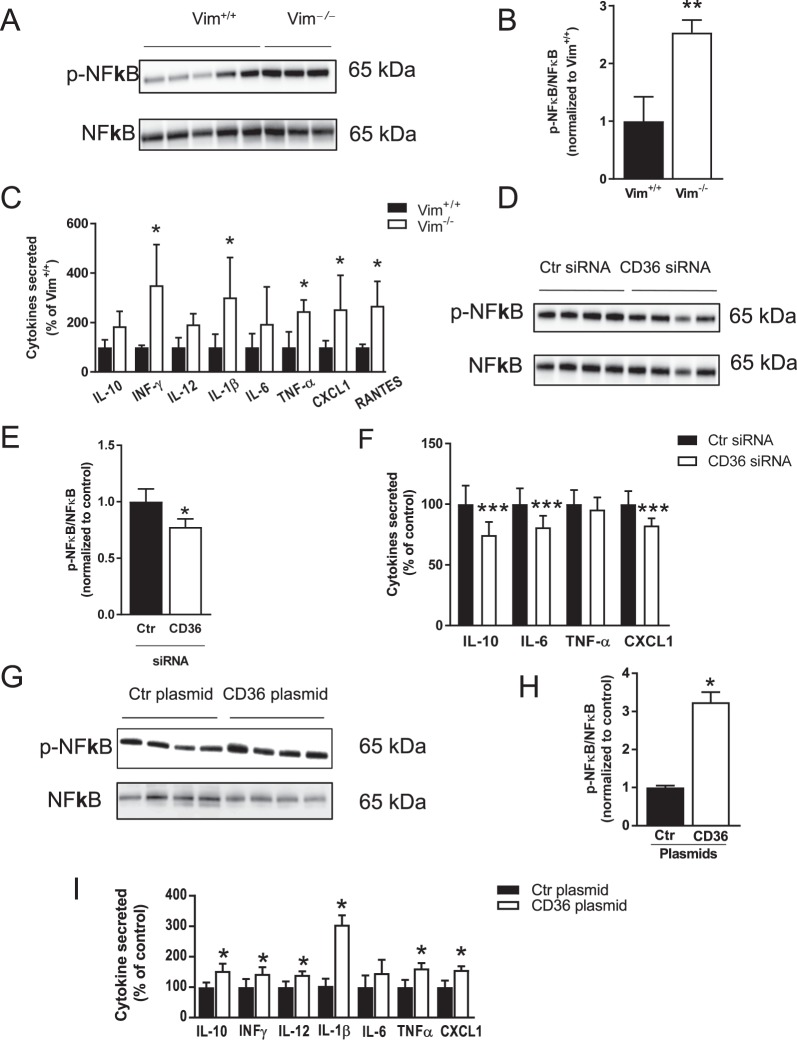
Figure 3.
The proinflammatory profile of Vim−/− macrophages is linked to CD36. (A,B) NFκB activation and (C). Cytokine secretion in bone marrow–derived macrophages from Vim−/− and wild-type mice. (D,E) NFκB activation and. (F) Cytokine secretion in in bone marrow–derived Vim−/− macrophages transfected with CD36 or control (Ctr) siRNA. (G,H) NFκB activation and (F). Cytokine secretion in bone marrow–derived macrophages from wild-type mice transfected with CD36 or control (Ctr) plasmids. NFκB activation was detected by immunoblotting using antibodies against phosphorylated p65 subunit of NFκB (pNFκB). Membranes were stripped and incubated with antibodies against total p65 subunit of NFκB (NFκB). The images are the crops of the full length blots. The full length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S9 and Supplementary Fig. S10. The secreted cytokines were detected in the cell supernatants. Interleukin 10 (IL-10), interferon gamma (INFγ), interleukin 12 p70 (IL-12), interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1) and Regulated on Activation, Normal T Cell Expressed and Secreted (RANTES). Results are shown as mean ± SD n = 3−8 *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001.