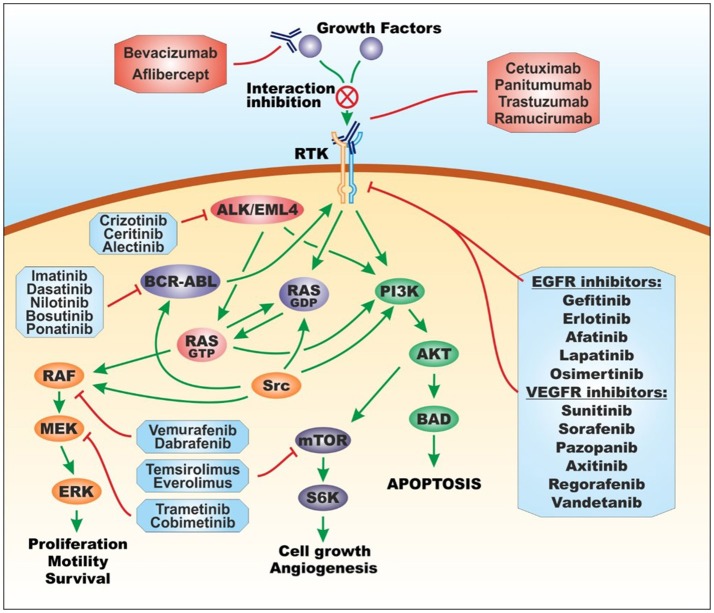
Figure 3.
Molecular targets of targeted therapy. Targeted therapy for cancer treatment is based on tyrosine and serine/threonine protein kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies. Protein kinase inhibitors are divided into EGFR inhibitors, VEGFR inhibitors, BCR/ABL inhibitors, ALK/EML4 inhibitors, RAF inhibitors, MEK inhibitors, and mTOR inhibitors. Monoclonal antibodies are directed toward extracellular growth factors or extracellular receptor tyrosine kinase. Figure 3 has been adapted and enriched by taking a cue from two published papers by Massimo Libra, co-author of the present review (Russo et al., 2014; Leonardi et al., 2018). For the general structure of Figure 3 and the name of drugs, the information contained in the book “Farmacologia: Principi di base e applicazioni terapeutiche” was taken into account (Rossi et al., 2016). ABL, Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog; AKT, protein kinase B; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; BAD, Bcl-2-associated death promoter; BCR, breakpoint cluster region; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; EML4, echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4; ERK, extracellular signal–regulated kinases; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RAF, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma kinase; RAS, RAS proto-oncogene GTPase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; S6K, S6 kinase; src, proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.