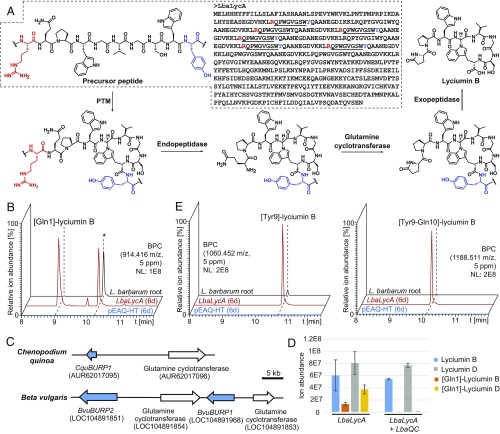
Fig. 3.
Investigation of lyciumin biosynthesis in Lycium barbarum. (A) Proposed biosynthetic pathway of lyciumin B in L. barbarum. (B) Detection of [Gln1]-lyciumin B mass signals in L. barbarum root extract and Nicotiana benthamiana leaf extracts after heterologous expression of lyciumin precursor LbaLycA for 6 d. Asterisk denotes ion source product of lyciumin B. (C) Genomic colocalization of lyciumin precursor genes and glutamine cyclotransferase genes for putative N-terminal lyciumin protection in Chenopodium quinoa and Beta vulgaris. (D) Detection of abolished mass signals for [Gln1]-lyciumin species in N. benthamiana leaf extracts after heterologous expression of lyciumin precursor LbaLycA and glutamine cyclotransferase LbaQC from Lycium barbarum root transcriptome (n = 3; error bars indicate ±1σ). (E) Detection of [Tyr9]-lyciumin B and [Tyr9-Gln10]-lyciumin B mass signals in L. barbarum root extract and N. benthamiana leaf extracts after heterologous expression of lyciumin precursor LbaLycA for 6 d. BPC, base peak chromatogram; LbaLycA (6 d), peptide extract of Nicotiana benthamiana infiltrated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404 containing pEAQ-HT-LbaLycA (6 d); pEAQ-HT (6 d), peptide extract of Nicotiana benthamiana infiltrated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404 containing pEAQ-HT (6 d); PTM, posttranslational modification.