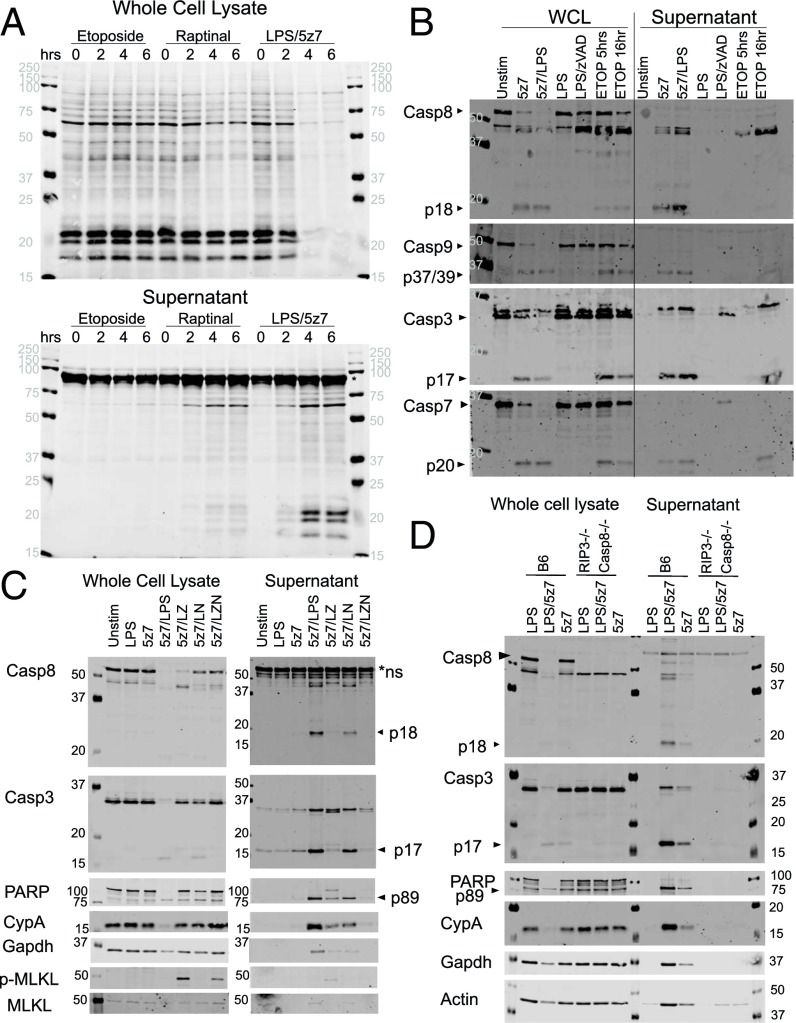
Fig. 2.
TAK1 inhibition results in necrotic cell death, exhibiting pan-caspase activation and the externalization of cytosolic content. (A) BMDMs were stimulated with etoposide (150 μM), raptinal (10 μM), or LPS (10 ng/mL)/5z7 (125 nM) for 0–6 h. Cellular lysates (Upper) and precipitated supernatant (Lower) were run on SDS/PAGE gels, and total protein was stained by LiCOR total protein stain. The asterisk indicates serum proteins from residual FBS in the culture medium. (B) BMDMs were stimulated as indicated for 5 h, except for etoposide, which was stimulated for an additional 16 h. Cellular lysate and precipitated supernatant were run on SDS/PAGE gels and were probed for pro- and cleaved forms of various apoptotic caspases. (C) BMDMs were stimulated with LPS/5z7 for 5 h in the presence of zVAD (50 μM) or Nec1 (10 μM) to block caspase or RIP kinase activity, respectively. Cellular lysate and precipitated supernatant were run on SDS/PAGE gels and probed for caspases, the caspase substrate PARP, cytosolic proteins cyclophilin A (CypA), Gapdh, phosphorylated (S345) MLKL (p-MLKL), and total MLKL. (D) BMDMs from B6 and Rip3−/− Casp8−/− animals were stimulated with LPS, LPS/5z7, or 5z7 for 5 h. Cellular lysate and precipitated supernatant were run on SDS/PAGE gels and probed for caspases, the caspase substrate PARP, cytosolic proteins cyclophilin A (CypA), Gapdh, and actin. All Western blots are representative of three or more experiments.