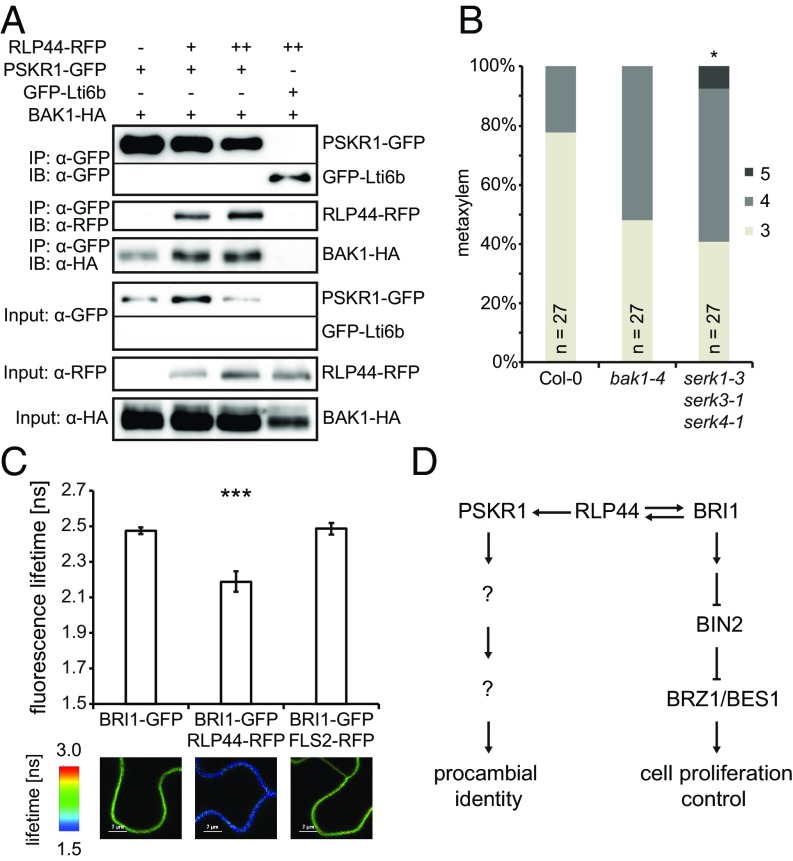
Fig. 4.
RLP44 promotes the association of LRR-RLKs and their coreceptor. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation analysis after transient expression in N. benthamiana leaves demonstrates an increased amount of BAK1-HA in PSKR1-GFP immunoprecipitates in the presence of RLP44-RFP. RLP44 levels were adjusted through increasing the density of Agrobacteria (denoted by + or ++). (B) Quantification of metaxylem cell number in bak1-4 and triple-serk mutants. Asterisks in C and D indicate statistically significant difference from Col-0 based on Dunn’s post hoc test with Benjamini–Hochberg correction after Kruskal–Wallis modified U test (*P < 0.05). (C) FRETFLIM analysis of the RLP44-BRI1 interaction in N. benthamiana leaves. Bars denote average of six to seven measurements ±SD. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference from BRI1-GFP and BRI1-GFP coexpressed with FLS2-RFP after pairwise t test (***P < 0.001). (D) Model of RLP44-mediated activation of PSK and BR signaling. RLP44 is capable of activating both signaling pathways, depending on the conditions, and is under transcriptional control by BRI1. Thus, BRI1 is required for RLP44-mediated control of procambial cell fate through PSK signaling.