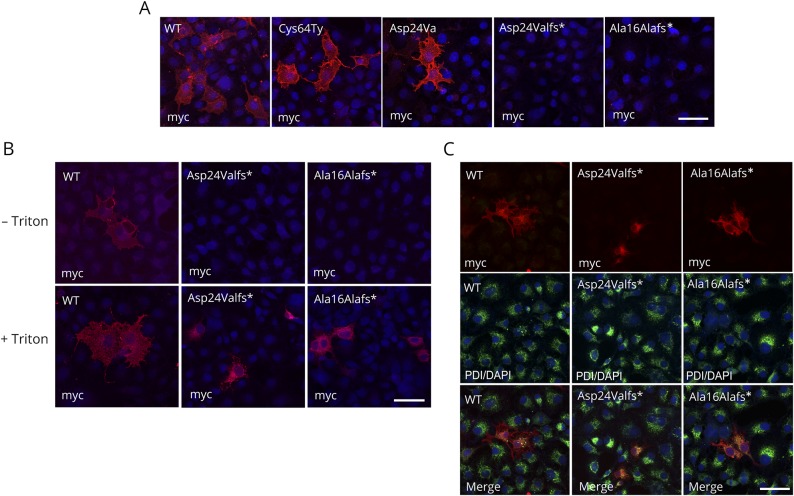
Figure 3. Surface and intracellular localization of hCD59 mutants.
(A) Characterization of WT and mutant Cys64Tyr, Asp24Val, Asp24Valfs*, and Ala16Alafs* constructs by myc antibody (red) and DAPI (blue). Staining with myc tag and secondary antibodies was added after fixation without Triton. (B) Characterization of WT and Asp24Valfs* and Ala16Alafs* CD59 mutants by anti-myc antibodies with or without Triton permeabilization. Differential recognition of WT and the Asp24Valfs* and Ala16Alafs* CD59 mutants by anti-myc. In both procedures, anti-myc detected the WT constructs with or without Triton, but in the mutant construct, ER staining was seen only with Triton. (C) Characterization of WT and Asp24Valfs* and Ala16Alafs* CD59 mutants by anti-myc and PDI antibodies. Upper panel: myc antibody (red); middle panel: PDI antibody (green) and DAPI (blue); and lower panel: merge. Cells were treated with methanol for permeabilization. Scale bars = 50 μm. PDI = protein disulfide isomerase; WT = wild type.