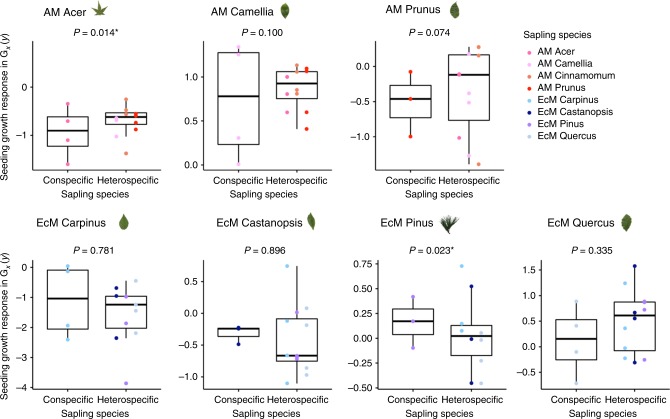
Fig. 3.
Comparison of seedling growth responses under conspecific versus heterospecific resident saplings in plant communities associated with matching mycorrhizal types. Growth response Gx(y) was calculated as the average of total seedling biomass (aboveground and belowground combined) of species measured in quadruplicate per sapling species per mesocosm. Based on the fitted linear mixed-effects model, linear contrasts were made between the ln-transformed total biomass Gx(y) of individual seedling species under conspecific versus heterospecific saplings of matching mycorrhizal types. In each seedling species, we used ln-transformed growth response of seedling species x, that is, ln[Gx(y)], as the response variable, sapling species identity y as a fixed-effects predictor, and block as a random-effects predictor: ln[Gx(y)] ~ sapling species + (1|block). Due to the slight modification of experimental design, the arbuscular mycorrhizal species Celtis sinensis occurred only as a seedling species not as a sapling species, so it was excluded from statistical analysis. The lines in each boxplot represent the minimum (whisker), lower quartile, median, upper quartile, and maximum (whisker)