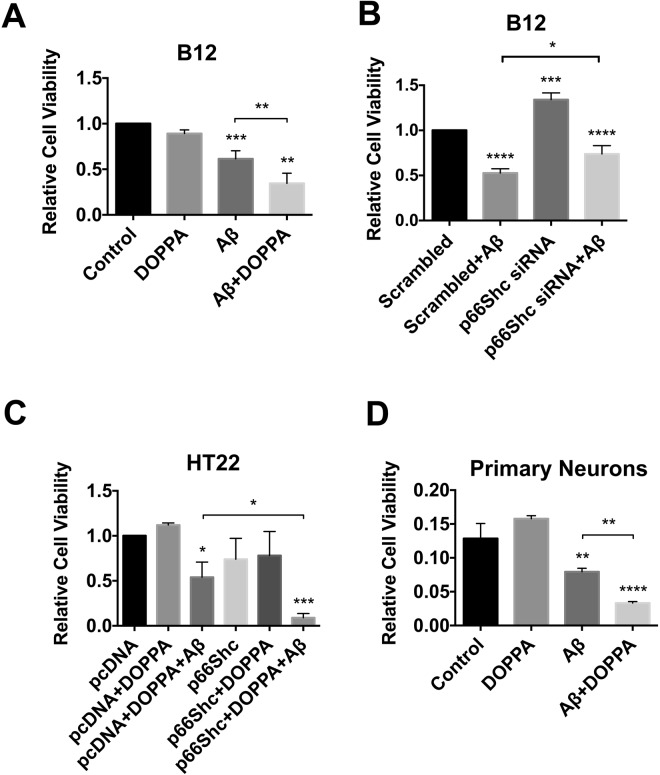
Figure 9.
p66Shc activation enhances Aβ toxicity. (A) Treatment of B12 cells with both Aβ1–42 (20 µM) and DOPPA (100 nM) was significantly more toxic than Aβ treatment alone. (B) Silencing of p66Shc expression in B12 cells led to reduced Aβ-induced toxicity compared to B12 cells transfected with control siRNA and treated with Aβ. (C) HT22 cells ectopically expressing p66Shc and treated with DOPPA (100 nM) exhibited significantly decreased viability following Aβ treatment compared to pcDNA control cells treated with both agents. (D) DOPPA induced activation of p66Shc exacerbated Aβ toxicity in mouse primary cortical neurons. Data presented are the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001).