Table 1. Reaction optimization using anisole a .
| |||||
| Entry | Catalyst b | Solvent c | Temperature (time) | Yield
d
(%) |
|
| 3aA | 2aA | ||||
| 1 | Ph3PAuCl/AgSbF6 | DCE | 80 °C (44 h) | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | IPrAuNTf2 | DCE | 80 °C (24 h) | 0 | 36 |
| 3 | XPhosAuCl/AgNTf2 | DCE | 80 °C (21 h) | 0 | 57 |
| 4 | BrettPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6 | DCE | 80 °C (30 h) | 0 | 65 |
| 5 | JohnPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6 | DCE | 80 °C (26 h) | 44 | 26 |
| 6 | JohnPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6 | Benzene | 80 °C (10 h) | 0 | 78 |
| 7 | JohnPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6 | Propan-2-ol | 80 °C (10 h) | 0 | 63 |
| 8 | JohnPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6 | 1,4-Dioxane | 80 °C (10 h) | 0 | 87 |
| 9 | JohnPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6 | TCE | 140 °C (13 h) | 55 | 0 |
| 10 | JohnPhosAu(MeCN)SbF 6 | TCE (condition A) | 80 °C (1 h), 140 °C (16 h) | 75 | 0 |
| 11 | BrettPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6 | Anisole | 80 °C (15 h) | 13 | 28 |
| 12 | BrettPhosAu(MeCN)SbF 6 | Anisole (condition B) | 140 °C (19.5 h) | 86 | 0 |
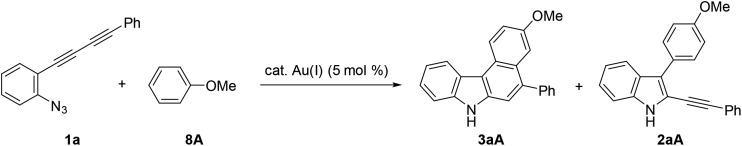
aReactions were carried out using 1a (1 equiv.), 8A (10 equiv.), and the gold catalyst (5 mol%).
bThe ligand structures are shown in Fig. 2. BrettPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6, JohnPhosAu(MeCN)SbF6, and IPrAuNTf2 were prepared in advance. The other catalysts were prepared in situ by mixing the AuCl ligand with AgNTf2 or AgSbF6.
cDCE = 1,2-dichloroethane, TCE = 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane.
dIsolated yields.
