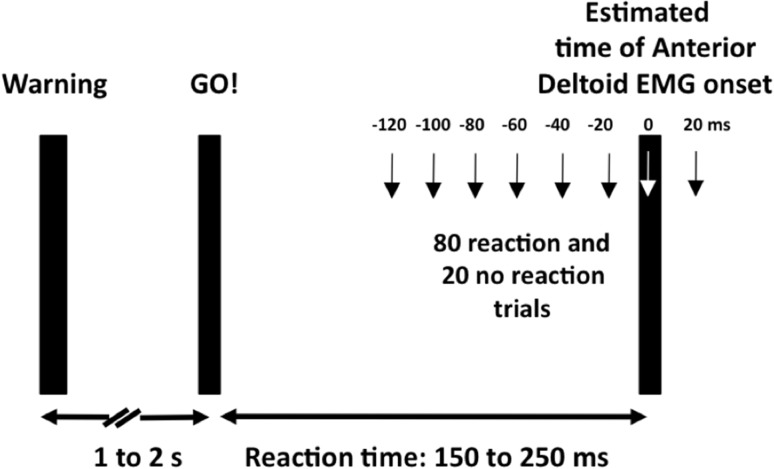
Fig. 1.
Experimental protocol to determine the effects of age (young, middle-aged, old) and posture (sitting, standing) on a spinal element of the anticipatory posture adjustment, APA. In 20 preliminary trials, we measured subjects’ reaction time in response to an auditory cue after a visual warning signal and also the onset of EMG activity of the anterior deltoid. Based on this estimated interval, we stimulated the posterior tibial nerve to evoke an H reflex in 80 reaction time trials (arm swing) and 40 dummy trials (no arm swing) in 20 ms intervals relative to the estimated anterior deltoid onset in sitting and also in standing. In response to the auditory GO! signal, subjects rapidly swung their right arm from the side of the body to a horizontal position, causing a self-perturbation. The warning signal was a light