Fig. 6.
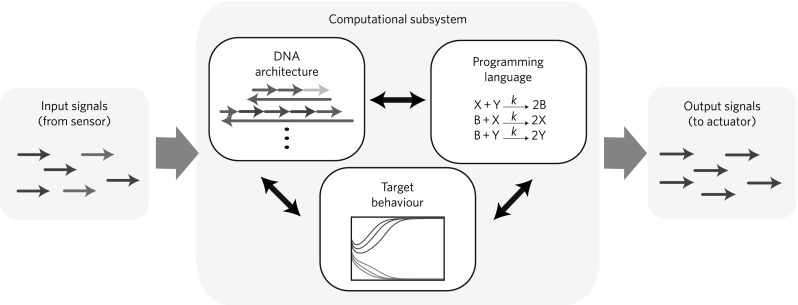
Implementation of a switch using a 2-domain DNA strand displacement encoding, reproduced from Chen et al. (2013a). The system takes as input two populations of signals, encoded as DNA strands, and uses a distributed consensus network to determine which population is in the majority. The output of the system is a homogeneous population of strands, in which all of the minority strands have been converted to the majority. As with the oscillator described in Fig. 5, the behaviour of the systems is specified as a chemical reaction network consisting of three reactions, in which X and Y cancel each other out to produce two intermediates B, species X converts B to itself, and species Y converts B to itself. This is equivalent to the Approximate Majority network (Angluin et al. 2008) described in Fig. 2
