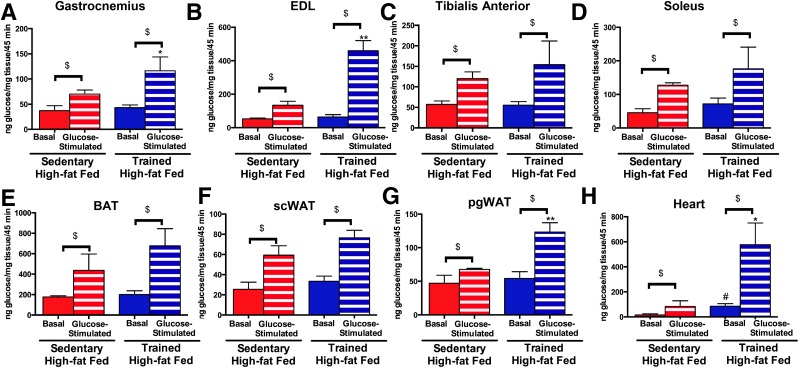
Figure 4.
Paternal exercise increases glucose-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, heart, and pgWAT in male offspring. A–H: In vivo glucose uptake was measured in 52-week-old male offspring of high fat–fed sedentary and trained sires. Mice were fasted overnight and anesthetized, and 0.33 µCi [3H]2-deoxyglucose/g body wt was administered via retro-orbital injection in the presence of saline (Basal) or 1 g/kg body wt glucose (Glucose). Glucose uptake was measured in the gastrocnemius (A), EDL (B), tibialis anterior (C), soleus (D), BAT (E), scWAT (F), pgWAT (G), and heart (H). Data are the mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 glucose-stimulated glucose uptake in offspring from high fat–fed exercise-trained sires compared with offspring from high fat–fed sedentary sires; #P < 0.05 basal glucose uptake in offspring from high fat–fed exercise-trained sires compared with offspring from high fat–fed sedentary sires; $P < 0.05 basal glucose uptake vs. glucose stimulated glucose uptake) (n = 6/group).