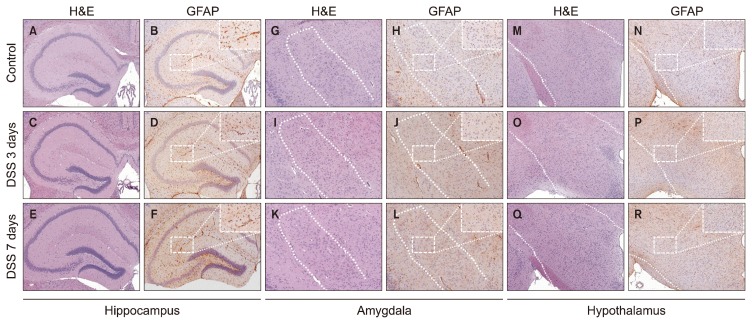
Fig. 5.
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression patterns in the hippocampus, amygdala and hypothalamus after exposure to dextran sodium sulfate (DSS). These are representative photomicrographs of the hippocampus (A–F), the amygdala (G–L) and the hypothalamus (M–R) from our study. Representative histology of the hippocampus was stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) at untreated (control) (A), 3 days (C), and 7 days (E) after exposed to DSS. GFAP expression in hippocampus tissue was increased compared to (B) control group after exposed to DSS at (D) 3 days, and (F) 7 days, as shown by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Representative histology of the amygdala was also stained with H&E at (G) untreated (control), (I) 3 days, and (K) 7 days after exposed to DSS. IHC of GFAP expression in the amygdala showed no significant difference between the (H) control group, (J) the 3-day treatment group, and (L) the 7-day treatment group. (M) Hypothalamus tissue stained with H&E at untreated (control), (O) 3 days, and (Q) 7 days after exposed to DSS. IHC of GFAP expression in the hypothalamus did not show any significant difference between (N) the control group, (P) the 3-day treatment group, and (R) the 7-day treatment group.